Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download the PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Water Class 6 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Questions
1. Define transpiration.
Answer: The loss of water from the leaves of plants into air in the form of water vapour is called transpiration.
2. Why is water called a universal solvent?
Answer: Water can dissolve a large amount of substances in it, therefore it is called a universal solvent.
3. What is water conservation?
Answer: Water conservation is the wise and judicious use of water
4. Define water cycle.
Answer: The cycle of the change of water to water vapour and back to water in nature is known as water cycle.
5. What is surface water?
Answer: The water present on the surface of earth, like in seas, rivers, etc. is called surface water.
6. Why is the water table going down in big cities?
Answer: Overuse of groundwater is the reason for decrease in water table.
7. Write the sources of water on the earth.
Answer: Sources of water on the earth are:
Seas, Oceans, Rivers, Springs, Tubewells, etc.
8. In which forms, water exists on the earth?
Answer: Water exists on the earth in all three physical forms: ice, water and water vapour.
9. What is transpiration?
Answer: Loss of water in the form of water vapour through stomata of leaves is called transpiration.
10. How are the clouds formed?
Answer: Clouds are formed by the condensation of water vapour at high altitude.
11. What is meant by the conservation of water?
Answer: Careful, economical and wise use of water and avoiding the wastage of water is called conservation of water.
Short Answer Type Questions
1: What would happen if we do not have easy access to water for a long period of time?
Answer: We would not be able to cook food, clean utensils, bath, wash cloth, clean floor, toilet works, brushing, and most important drinking.
2: List all the activities for which you need water in a day.
Answer: We need water for so many activities like cook food, clean utensils, bath, wash cloth, clean floor, toilet works, brushing, and most important drinking.
3: List some more use of water, apart from our daily activities in which water is required.
Answer: We obtain food from plants, plants need water to grow and cook their food by the process of photosynthesis. Water is used in industries for processing large number of things that we use like fabrics, paper etc.
4: From where do we get water?
Answer: We get water from water bodies like river, spring, pond, well and hand pump. Although the rain water is the natural source of water that fulfil various water bodies.
5: Why water in oceans and seas are unfit for drinking?
Answer: Water in ocean and seas are salty because, many salts are dissolved in it, so it is unfit for drinking.
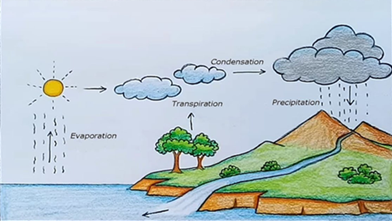
6: Draw a labelled diagram of water cycle.
Answer:
7: Why water spilled on a floor dries up after sometime?
Answer: Water spilled on floor dries up after sometimes because of the process of evaporation.
8: Why evaporation takes place from all open surfaces of water?
Answer: Evaporation takes place in presence of sunlight, that heats up the open water surface and convert it into water vapour.
9: What is transpiration?
Answer: The process of loss of water from the aerial part of plants like leaves is called transpiration.
11: Why rain clouds are dark in colour?
Answer: Rain cloud is dark because their water drops are larger and less transparent
14: What is ground water?
Answer: Ground water is the water located beneath the earth’s surface in soil and in the fractures of rock formations.
16: What happens if it rains heavily?
Answer: Excess of rainfall leads to many problems. It raises the water level in rivers, lakes and ponds. The water may then spread over larger area causing the situation of floods. The crop fields, forests, villages and cities may get submerged by water.
17: What happens if it does not rain for a longer period of time?
Answer: If it does not rain for a longer period of time then the water level in rivers, lakes and ponds will go down, some of them may even dry up. The ground water also becomes scarce. This may lead to draught.
18: Suggest some methods to conserve water.
Answer: By making wise and judicious use of available water, we can save water. We should not waste water and try to harvest rain water.
19: To clean their spectacles, people often breathe out on glasses to make them wet, explain why the glasses becomes wet.
Answer: The most air coming out from mouth condenses on glasses to make glasses wet.
20: A cooled bottle of water kept outside refrigerator, shows puddle of water around it. Explain why?
Answer: The cool surface of cooled bottle cools the air around it and the water vapours of the air condenses on the surface of the bottle.
21. Are there regions where people do not get adequate amount of water? How do they manage?
Answer: Hot and dry regions like Rajasthan do not get adequate amount of water. They have to travel long distances for collecting drinking water.
22. Why do some water pipes burst in winters?
Answer: During winters water freezes, which develops enormous pressure in the pipe. Due to this high pressure, water pipes burst.
23. Why do wet clothes placed on a clothes line get dry after some time? Explain.
Answer: Water present in wet clothes is converted into water vapour due to evaporation and leaves them dry.
24. Water kept in sunlight gets heat from sun and is evaporated. But how does water kept under the shade of a tree also gets evaporated? Explain.
Answer: Air around us gets heated from sunlight. This warm air provides heat for evaporation of water kept in the shade.
25. How do the areas covered with concrete affect the availability of ground water?
Answer: Areas covered with concrete reduce the seepage of rain water into the ground and this reduces the availability of groundwater.
26. Why is there a need for conserving water? Give two reasons.
Answer: (i) Increasing population needs more water.
(ii) Availability of water is decreasing day-by-day.
27. How can the states of water be interchanged?
Answer: On heating, ice (solid water) changes into liquid water and then into water vapour. On condensation, vapours convert into liquid and on freezing, liquid water forms ice.
28. Mention two main functions of water for living organisms.
Answer: Two main functions of water for living organisms are:
- Water is essential for the germination of seeds, growth of plants and in photosynthesis.
- Water is used for the transportation of people and goods.
29. Why is ocean water not suitable for domestic use?
Answer: Sea and ocean water contains large amounts of various salts. It is due to these salts the ocean water is salty and cannot be used for drinking, washing and for irrigation purposes.
30: Why does the water split on the floor disappear after some time?
Answer: Due to evaporation the water split is changed into water vapour. So it disappears after some time.
31. How does heavy rain affect us?
Answer: Heavy rains may cause:
- A rise of water level in dams, rivers, lakes, etc.
- Waterlogging and floods.
- Floods cause damage to property, crops and animals.
32. How does the failure of rainfall affect people on the earth?
Ans: The failure of rainfall can cause the following:
- The soil becomes dry.
- Water level in rivers, lakes, dams, etc. may fall. Ponds and canals may even dry up.
- The ground water level falls.
33. Name two processes responsible for the formation of clouds.
Answer: Evaporation and transpiration.
34. During winters why do we see more fog in close areas where there are lot of trees?
Answer: Due to lots of trees, air at that place contains much more water vapour during winters. These vapours condense on dust or smoke particles forming thick fog.
35. Dissolve two spoons of common salt in half a cup of water. Now if you want
to get the salt back, what will you do?
Answer: Water can be removed from the salt solution by heating it on a stove or keeping it in the sun in a plate for few hours. The water will be evaporated leaving behind the salt.
Long Answer Type Questions
1: Explain water cycle.
Answer: The Water Cycle is the journey of water from the land to the sky and back again.
There are six important processes that make up the water cycle.
(i) Condensation: the opposite of evaporation. Condensation occurs when a gas is changed into a liquid.
(ii) Infiltration: Infiltration is an important process where rain water soaks into the ground, through the soil and underlying rock layers.
(iii) Runoff: Much of the water that returns to Earth as precipitation runs off the surface of the land, and flows downhill into streams, rivers, ponds and lakes.
(iv) Evaporation: the process where a liquid, in this case water, changes from its liquid state to a gaseous state.
(v) Precipitation: When the temperature and atmospheric pressure are right, the small droplets of water in clouds form larger droplets and precipitation occurs. The raindrops fall to Earth.
(vi) Transpiration: As plants absorb water from the soil, the water moves from the roots through the stems to the leaves. Once the water reaches the leaves, some of it evaporates from the leaves, adding to the amount of water vapour in the air. This process of evaporation through plant leaves is called transpiration.
2. Most of the water that falls on the land as rain and snow, sooner or later goes
back to a sea or an ocean. Explain how it happens.
Answer: Snow in the mountains melt into water. This water flows down the mountains in the form of streams and rivers. Some of the water that falls on land as rain, also flows
in the form of rivers and streams. Most of the rivers cover long distances on land
and ultimately fall into a sea or an ocean.
3. Distinguish between the following.
(i) Flood and Drought
Answer: Flood: Condition when continuous rains cause water run-off that cannot be carried in river channels or retained in reservoirs.
Drought: Condition of abnormally dry weather within a geographic region where some rain is usually expected.
(ii) Evaporation and Condensation
Answer:
| Evaporation | Condensation |
| The process of changing water from liquid form to its vapour form. | The process of conversion of vapour into liquid form of water. |
(iii) Surface water and Groundwater
Answer:
| Surface water | Groundwater |
| Water collected on the ground or oceans and streams. | Water collected beneath the ground between the soil particles. |
4. Write four ways of conserving water.
Answer:
- Use a bucket for taking bath.
- Collect rainwater.
- Get all leaking pipes repaired.
- Instead of washing the floor, use a mop.
5. Write the disastrous effects of floods.
Answer:
- Floods damage property.
- Floods endanger lives of humans and animals.
- Floods cause soil erosion.
- Navigation is impaired.
6. What is meant by conservation of water? Suggest three methods to conserve water.
Answer: Careful and economical use of water and avoiding its wastage is called conservation of water.
Suggestions for conserving water:
- Use only the required quantity of water.
- Trees and forests help in causing rainfall. So to conserve water, we should plant more and more trees.
- By collecting rainwater in tanks, ponds or by constructing check dams.
7. What is rainwater harvesting? Describe the method of rainwater harvesting.
Answer: Rainwater harvesting is the collection of rainwater and storing for future use. In this system rainwater in collected from the rooftops by means of pipes into storage tank for later use.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting:
- Rooftop rainwater harvesting. In this system, the rainwater from the rooftop is collected in a storage tank, through pipes.
- Another method, a big pit is dug near house for collecting rainwater. This pit is filled with different layers of bricks, coarse gravels and sand or granite pieces.
8: How are clouds formed?
Answer: The water vapours present in sky are gas and cannot be seen. When air is cooled for some reason, each water vapour gathers and tie with neighbouring water vapour. Thus, vapor forms many water drops, each of which consists of many water molecules. One drop is very small and can float in the air. (But when a drop is large enough, they begin to fall as rain.) It cannot be seen but when very large number of drops gather they are visible like fog or smoke. This is cloud. There are many chances when cloud is formed. For example: towering thundercloud is formed when air rises high up in the sky.
9: What is dew and how it is formed?
Answer: On a clear day, water evaporates from the warm ground into the atmosphere. When night falls, the ground radiates the day’s warmth into the skies. The ground becomes much cooler, causing the water vapour to condense. This condensed vapour is dew.
10: What happens to the water that rain and snow bring to different regions of earth?
Answer: Some of the water flows in the form of rivers and streams, the rain water also fills up the lakes and pond, a part of rain water gets absorbed by the ground and seems to disappear in the soil. Some of this water is brought back to the air by the process of evaporation and transpiration.
11: How can we harvest rain water?
Answer: Roof top rain water harvesting- in this system rain water is collected from roof top to a storage tank through pipes. There is one more method in which rain water is allowed to go into the ground directly from the road side drains that collect rain water.
12: When does a draught occur?
Answer: If it does not rain for a longer period of time then the water level in rivers, lakes and ponds will go down, some of them may even dry up. The ground water also becomes scarce. This may lead to draught.