Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Maps Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Maps Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Questions
1: If the location of a post office has to be marked on a map, the symbol used will be_______.
Answer: PO
2: Where does east lies on the map?
Answer: right of north direction.
3: What type of map you will carry when you are going for trekking to the Himalayas?
Answer: physical maps.
4: Political maps show climatic zone. True/ False
Answer: False
5: Define a map.
Answer: A map is a representation or a drawing of the earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on a flat surface according to a scale.
6: What is thematic map?
Answer: Some maps focus on specific information such as road maps, rainfall maps, distribution of forests, industries etc. These are called thematic maps.
7: What are the Component of a map?
Answer: Free hand drawing, sketch
8: If you have to show Asia on paper, then the appropriate map will be
a) small scale map.
b) large scale map.
c) medium scale map.
d) free hand diagram of Asia.
Answer: (a) small scale map.
9: The number of major directions are _____.
Answer: Four
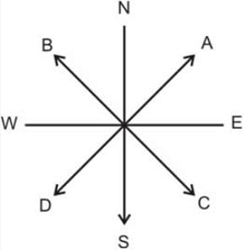
10: The arrow which is specified by A gives direction of ____________.
Answer: North east
11: Suppose a person is walking towards north and he takes left hand turn. Now he is moving in which direction?
Answer: West
12: The magnetic needle of compass gives direction of north-south. True/False
Answer: True
13: Meter gauge is represented by which symbol?
Answer: ![]()
14: Which symbol is used to show international boundaries?
Answer: ![]()
15: ![]()
The symbol represents __________.
Answer: Bridge
16: What do you understand by symbol![]()
Answer: Church
17: How will you show a graveyard on the map using symbol?
Answer: ![]()
18: A scale is mostly used in_____.
Answer: map.
19: Name the map that represents various relief features.
Answer: Physical map
20: A North Line is a line showing________ direction.
Answer: North
21: Name the colour which represents water bodies on the map.
Answer: Blue
22: What is a plan?
Answer: A detail drawing of small areas on a large scale.
23: If we have to find a city in the state of Andhra Pradesh, what type of map we will look for?
Answer: political map
24: Define a globe.
Answer: A globe is a true model of the earth.
25: A map has a
(a) diagram.
(b) plan.
(c) sketch.
(d) scale.
Answer: (d) Scale
26: What is an Atlas?
Answer: When many maps are put together we get an Atlas.
27: Maps provide more information than a globe. True/False
Answer: True
28: How symbols are useful for a map?
Answer: It makes the map simple to read.
29: An arrow shows______.
Answer: Direction
30: On a map, the scale given is 1 cm = 10 km. On the map the distance between your home and the temple is 3 cm then what will be the distance between temple and your home?
Answer: 30 km.
31: Which symbol show that an area has a lot of plant cover?
Answer:
32: Rahul wants to go to his uncle’s place that is in the NE direction and Rahul is in the N direction facing S, then the direction that he should turn to ______.
Answer: left.
33: Mohan is traveling by car. He sees a symbol ![]() .
.
That means he is moving towards a______.
Answer: Canal
34: A small distance on paper represents a large distance on the ground. True/False
Answer: True
35: On a map, the scale given is 1 cm = 500 m, the type of map used will be
a) thematic map.
b) relief map.
c) small scale map.
d) large scale map
Answer: (d) large scale map
36: A sketch is true in its
a) shape
b) size
c) location
d) scale
Answer: (c) location
37: Which map has more information, small-scale maps or large scale maps?
Answer: large-scale map
38: The plain areas of the world are represented by_______ colour.
Answer: green
39: Which map will be used to show Distribution of industries in Europe?
Answer: thematic maps
40: Which colour is used to show Plateau on the map?
Answer: Yellow colour
Short Answer Type Questions
1: Why are conventional symbols used in maps?
Answer: It is the third important component of a map. The maps have to depict a number of features, e.g. buildings, trees, villages etc. It becomes difficult to draw them because of their shape and size. Thus symbols are used to depict various physical features. With the use of these symbols, maps can be drawn easily and are simple to read. There is an international agreement regarding the use of these symbols.
2: What do you understand by the scale of the map?
Answer: The scale is the relation between distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground, e.g. if the distance on the map and grounds of same two points is 1 cm and 1km receptively, the scale of the map will be 1cm to 1km, R.F= (1:1000000). Scale is very important in any map. If you know the scale, you will be able to calculate the distance between any two places on a map.
3: List the three main components of a map.
Answer: 1. Scale 2. Direction 3. Symbol.
4: List the ways in which the globes are more useful than maps.
Answer: Globes are preferred more useful than maps because of the reasons given below:
1. It shows the poles, latitudes, longitudes, oceans and continents in their correct shape.
2. There are globes which show various relief features like mountains, plateaus and plains.
3. It also shows distance between the two adjoining meridians which decreases as one goes away from the equator towards the poles.
5: Write short notes on a compass.
Answer: A compass is a very simple instrument used to find out the direction of a place. It has a magnetic needle, which rotates freely in a horizontal place and is balanced on a fine point. The magnetic needle always points toward north-south direction.
6: Explain the advantages of using maps?
Answer:
- Maps can show more details
- Many maps when put together make an atlas and show various continents, countries and can provide information about any particular aspect.
- Maps can be drawn in small scale as well as in large scale.
- Maps can be folded / rolled and are easily portable.
7: Explain the Thematic maps.
Answer: Some maps may focus on specific information of the regions, for example rainfall maps, road maps, tourist map and topographical maps. Such maps represent a particular topic or theme and are called thematic maps.
8: Why political maps use more number of colours as compared to physical map?
Answer: Political maps, which show more human created features (especially boundaries), usually use more colours than physical maps, which represent the landscape often without regard for human modifications.
9: Write about the shortcomings of a globe?
Answer: A globe cannot show as many details as a map can. It does not give details of any country and details like districts, states, town or villages. It is also heavy and difficult to carry around.
10: Differentiate between physical map and political map.
Answer:
| Physical Map | Political Map |
| A physical map is one that shows physical features of the earth like mountains rivers, vegetation, plateaus etc. | Political map shows the different countries and states of the world with their boundaries, cities and towns. |
11: Differentiate between a map and a plane.
Answer:
| Map | Plan |
| In the map, details are given in the form of symbols words, lines and colours. | Plan is drawn to large scale and shows true direction. |
| It shows a large area of ground on a small scale or large scale, i.e., maps reduce the entire world on its parts to fit on a sheet of paper. Maps are precise. | It shows detailed layout of spaces, length and breadth in a building etc. Its scale can be enlarged. |
12: What is the easiest way to remember compass directions?
Answer: The earth rotates west to east, so the sun rises in the east and sets in the west. No matter which side one is facing, east is the morning sun and west is the evening sun or night time.
13: What are the various advantages of globes?
Answer:
- Globes give a good, visual indication of the earth’s surface.
- The shape of the continents and their relative positions are correct.
- Gives a true representation; whatever position it is viewed from.
- The shape and size of the various continents is not distorted as compared to representing a spherical surface on a flat piece of paper.
14: What are conventional symbols?![]()
Answer: Conventional Symbols are symbols that are used on maps to represent different features.
15: Define political maps
Answer: Map which shows cities, towns, villages, different countries and states of the world with their boundaries are called political maps.
16: What is a scale? How many types of scales are there?
Answer: A scale is ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. It is of three types:
i) Statement of a scale
ii) Representative Fractions (RF)
iii) Graphical scale
17: What do the following colours represents on the map?
Blue, Red, Yellow, Green, Brown and Black
Answer: Blue – lakes, rivers, streams, oceans, reservoirs, etc.
Red – major highways, roads, urban areas, airports, special interest sites, military sites, place names, buildings, borders.
Yellow – built-up or urban areas.
Green – parks, golf courses, forest, orchards, highways. Brown – deserts, historical sites, national parks, military reservations or bases, contour (elevation) lines. Black – railroads, highways, bridges, place names, buildings, borders.
Long Answer Type Questions
1: What are the basic characteristics of a good map?
Answer: Maps are the basic tools of geography that enable us to depict spatial phenomenon on paper. A good map will have:
1. Legend: A good map will have a legend or key which shows the user what different symbols mean. For instance, a square with a flag on top usually represents a school and roads are represented by a variety of widths and combinations of lines.
2. Direction: Without a north arrow, it is difficult to determine the orientation of a map. With a north arrow (pointing in the correct direction), a user can determine direction.
3. Title: A map’s title provides important clues about the cartographer’s intentions and goals.
2: Why do we need to understand maps?
Answer: Maps are used:
1. To find our way around a city.
2. To find the location of specific places in a new city.
3. To find the shortest route to a specific spot.
4. To find out locations of petrol pumps, police station and rest house on highways.
5. In case of emergency, it helps to find the nearest hospital or medical aid.
3: What is the difference between the magnetic North Pole and geographical North Pole?
Answer: The North Pole (true north) is a geographic pole with a stationary location at 90-degrees north. This geographic North Pole is the fixed northernmost point on earth from which all points lie south.
The Magnetic North Pole is not based on true north, but on the magnetosphere of the planet. The Magnetic North Pole lies hundreds of miles away from the true north, with its exact position constantly shifting.
4: How can you measure distance on the map?
Answer: Maps not only help us to locate a place but also help us to find distance between two places in the following ways:
1) Find the scale for the map you are going to use. It might be ruler looking bar scale or a written scale in words or numbers.
2) Use a ruler to measure the distance between the two places. If the line is quite curved, use a string to determine the distance and then measure the string.
3) If the scale is a word statement, i.e., ‘One centimeter equals one kilometer’ then determine the distance.
5: Mention some of the disadvantages of magnetic compass?
Answer: The compass is very stable in areas close to the equator, which is far from “Magnetic North”. At some point close to the Magnetic Pole, the compass will not indicate any particular direction but will begin to drift in a non direction indicating manner. Also, the needle starts to point up or down when getting closer to the poles, due to the so-called magnetic inclination. Cheap compasses with bad bearings may get stuck due to this; therefore, indicate a wrong direction.