Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Soil Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Extra Questions and Answer
1. Name the best soil for growing plants.
Answer: Loamy soil
2. What is soil?
Answer: The mixture of rock particles and humus is called the soil.
3. Which type of soil is well aerated?
Answer: Sandy soil is well aerated.
4. Which soil has the highest percolation rate?
Answer: Sandy soil has the highest percolation rate.
5. Which soil has the least percolation rate?
Answer: Clayey soil has the least percolation rate.
6. What is humus?
Answer: The rotting dead matter in the soil is called humus.
7. What is soil?
Answer: The mixture of rock particles and humus is called the soil.
8. Name some soil pollutants.
Answer: Polythene bags, plastics, waste products, chemicals and pesticides.
9. Which soil horizon contains humus?
Answer: Topsoil or the A-horizon
10. Which soil horizon has a lesser amount of humus but more of minerals?
Answer: B-horizon or the middle layer
11. Which type of soil is the best for making pots, toys and statues?
Answer: Clayey soil is used to make pots, toys and statues.
12. What kind of soil should be used for making matkas and surahis?
Answer: Clayey soil should be used for making matkas and surahis.
13. Why the uppermost horizon is generally dark in colour?
Answer: The uppermost horizon is generally dark in colour as it is rich in humus and minerals.
14. What is the role of humus in the soil?
Answer: The humus makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to growing plants.
15. What is soil profile?
Answer: A vertical section through different layers of the soil is called the soil profile.
Short Extra Questions and Answers
1. What is loamy soil?
Answer: Loamy soil is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle known as silt.
2. What is bedrock?
Answer: Just below the C-horizon is the bedrock, which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade.
3. Which type of soil is best for growing wheat and gram?
Answer: Clayey and loamy soils are both suitable for growing cereals like wheat and gram.
4. Which areas experience more severe soil erosion?
Answer: Erosion of soil is more severe in areas of little or no surface vegetation, such as desert or bare lands.
5. Which type of soil is best for growing lentils?
Answer: For lentils (masoor) and other pulses, loamy soils, which drain water easily, are required.
6. Which type of soil is best for growing cotton?
Answer: For cotton, sandy loam or loam, which drain water easily and can hold plenty of air, are more suitable.
7. Wheat are grown in the fine clayey soils. Give reason.
Answer: Crops such as wheat are grown in the fine clayey soils, because they are rich in humus and are very fertile.
8. Classify the soil on the basis of the proportion of particles of various sizes.
Answer: On the basis of the proportion of particles of various sizes, the soil can be classified as sandy, clayey and loamy.
9. What is called soil moisture?
Answer: Soil holds water in it, which is called soil moisture. The capacity of a soil to hold water is important for various crops.
10. State the factors on which nature of the soil depends?
Answer: The nature of any soil depends upon the rocks from which it has been formed and the type of vegetation that grows in it.
11. What is silt?
Answer: Silt occurs as a deposit in river beds. The size of the silt particles is between those of sand and clay.
12. Explain how soil is formed.
Answer: The soil is formed by the breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate. It is a very slow process.
13. Why do air above the soil shimmer on a hot summer day?
Answer: On a hot summer day, the vapour coming out of the soil reflects the sunlight and thus, the air above the soil seems to shimmer.
14. Which type of soil is best for growing paddy?
Answer: For paddy, soils rich in clay and organic matter and having a good capacity to retain water are ideal.
15. What is weathering?
Answer: Soil is formed by the breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate. This process is called weathering.
16. Which type of soil retains the highest amount of water and which retains the least?
Answer: Clayey soil retains the highest amount of water and sandy soil retains the least.
17. Which natural resource supports the growth of plants by holding the roots firmly and supplying water and nutrients?
Answer: Soil supports the growth of plants by holding the roots firmly and supplying water and nutrients.
18. How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Answer: Clayey soil is useful for crops because:
- It is good at retaining water.
- It is rich in organic matter.
19. What affect the soil profile and bring changes in the soil structure?
Answer: Soil is affected by wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity. These are some important climatic factors which affect the soil profile and bring changes in the soil structure.
20. Why is top soil known as the habitat of many living organisms?
Answer: Top soil is known as the habitat of many living organisms because this provides shelter for many living organisms such as worms, rodents, moles and beetles.
21. Why is the topsoil important for plant growth?
Answer: Top soil is important for plant growth because it is rich in humus and minerals which makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to growing plants.
22. Why there is a demand to ban the polythene bags and plastics?
Answer: Polythene bags and plastics pollute the soil. They also kill the organisms living in the soil. That is why there is a demand to ban the polythene bags and plastics.
Long Extra Questions and Answers
1. What are called horizons?
Answer: A vertical section through different layers of the soil is called the soil profile. Each layer differs in feel (texture), colour, depth and chemical composition. These layers are referred to as horizons.
2. What are the properties of loamy soil?
Answer: Properties of loamy soil are as following:
- The best topsoil for growing plants is loam. Loamy soil is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle known as silt.
- The loamy soil also has humus in it.
- It has the right water holding capacity for the growth of plants.
3. What are the properties of clayey soil?
Answer: Properties of clayey soil are as follows:
- Clay particles, being much smaller, pack tightly together, leaving little space for air.
- Water can be held in the tiny gaps between the particles of clay. So clay soils have little air.
- They are heavy as they hold more water than the sandy soils.
4. Why is soil regarded as one of the most important natural resources?
Or
Why is soil an inseparable part of our life?
Answer: Soil is one of the most important natural resources. It supports the growth of plants by holding the roots firmly and supplying water and nutrients. It is the home for many organisms. Soil is essential for agriculture. Agriculture provides food, clothing and shelter for all. Soil is thus an inseparable part of our life.
5. What are the properties of sandy soil?
Answer: Properties of sandy soil are:
- Sand particles are quite large.
- Sand particle cannot fit closely together, so there are large spaces between them. These spaces are filled with air. So, the sand is well aerated.
- Water can drain quickly through the spaces between the sand particles. So, sandy soils tend to be light and dry.
6. Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation. She observed that it took 40 min for 200 mL of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.

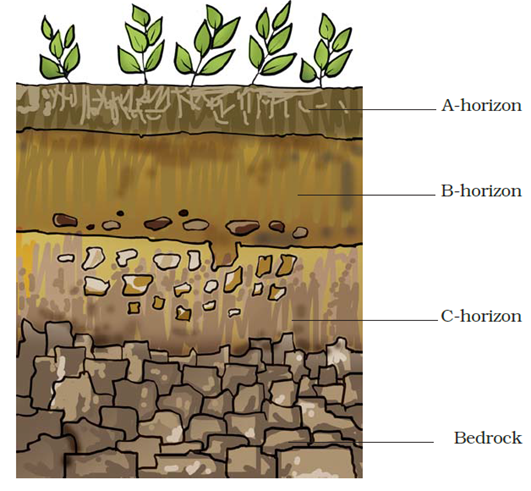
7. Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Answer:
8. List the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil.
Answer:
| Clayey soil | Sandy soil |
| 1. Clay particles are much smaller. | 1. Sand particles are quite large. |
| 2. Clayey soils tend to be heavy as they hold more water than the sandy soils. | 2. Sandy soils tend to be light as water drain quickly through the spaces between the sand particles. |
| 3. Clay particles pack tightly together, leaving little space for air. | 3. They cannot fit closely together, so there are large spaces between them. These spaces are filled with air. |
| 4. Clayey soil is more fertile compared to sandy soil. | 4. Sandy soil is less fertile compared to clayey soil. |
9. Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Answer: Steps to prevent soil pollution are:
- The polythene bags and plastics should be banned.
- Waste products and chemicals should be treated before they are released into the soil.
- The use of pesticides should be minimised.
- Use of organic manure, fertilizers, and milder pesticides for agricultural activities should be encouraged.
Steps to prevent soil erosion are:
- Planting more and more trees.
- Terrace farming.
- Retaining walls can be built around the area of erosion to prevent water run-off.
- Making people aware of pros and cons of deforestation.
10. Describe the different layers of soil profile.
Answer: Different layers of soil profile are:
- The uppermost horizon is generally dark in colour as it is rich in humus and minerals. The humus makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to growing plants. This layer is generally soft, porous and can retain more water. It is called the topsoil or the A-horizon. This provides shelter for many living organisms such as worms, rodents, moles and beetles. The roots of small plants are embedded entirely in the topsoil.
- The next layer has a lesser amount of humus but more of minerals. This layer is generally harder and more compact and is called the B-horizon or the middle layer.
- The third layer is the C-horizon, which is made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices.
- Below this layer is the bedrock, which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade.