Star and Solar System Class 8 Important Questions and Answers
Important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Star and Solar System is given below. These important questions will help students while preparing for the exam. Practising these important questions will analyse their performance and work on their weak points. Score well in exam of Class 8 Science by going through these important questions. Students of Class 8 can download important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Star and Solar System PDF by clicking the link provided below.
Important Questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Star and Solar System
Here you can get Class 8 Important Questions Science based on NCERT Text book for Class 8. Science Class 8 Important Questions are very helpful to score high marks in board exams. Here we have covered Important Questions on Star and Solar System for Class 8 Science subject.
Very Short Answers Questions
1. Name the planet appears in the northern sky before sunrise?
Answer: Venus brightest of all planets.
2. Name the planet which has 28 moons?
Answer: Jupiter mainly consists of hydrogen and helium gases
3. In which direction stars move except Polar star?
Answer: When seen from earth stars appears to move from east to west.
4. Why pole star appears stationary?
Answer: As it lies on the imaginary axis of the rotation of the earth.
5. Which two planets have asteroids between them?
Answer: asteroids are the rocks pieces that revolve around the sun between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter.
6. Which comet visits the earth after 76 years?
Answer: Halley’s Comet. Heavenly bodies that revolve around the sun and appears as bright as the glowing ball with a long tail is called a comet.
7. What happens to meteors when enters the earth’s atmosphere?
Answer: meteors when enters the earth’s atmosphere starts glowing and are seen as a bright streak of light fleshing momentarily across the sky.
8. What is the high tog geostationary satellite from the earth surface?
Answer: 36000km and used for satellite communications.
9. What does term INSAT mean?
Answer: Indian National Satellite.
10.Name the first Indian satellite launched successfully.
Answer: Aryabhata on 19 April 1975
11. What is sun?
Answer: The sun is a star.
12. Name the planet nearest to the ‘sun’.
Answer: Mercury.
13. Name the planet nearest to the earth.
Answer: Mars.
14. Name the planets opposite side of the earth.
Answer: Mars and Venus.
15. Name the star which is nearest to the earth.
Answer: Alpha Centaury.
16. Write the name of any two constellations.
Answer: Great Bear and Orion.
17. Which planet has rings around it?
Answer: Saturn.
18. Name the planet farthest from the sun.
Answer: Neptune.
19. Write the name of the astronaut who first landed on the moon.
Answer: Neil Armstrong.
20. When did Neil Armstrong land on the surface of the moon?
Answer: On July 21, 1969.
21. What is the speed of light?
Answer: 300000 km per second.
22. Write the other name of constellation Great Bear.
Answer: Saptarishi.
23. How many bright stars are there in Orion?
Answer: Seven or Eight.
24. What is the other name of Orion?
Answer: Hunter.
25. Which is the nearest star to the earth?
Answer: Sun.
26. Which star is called morning or evening star?
Answer: Venus.
27. Which colour is seen on earth from space?
Answer: Blue green.
28. Which planet is called Red planet?
Answer: Mars.
29. Which is the smallest planet?
Answer: Mercury.
30. Which planet is yellowish in colour?
Answer: Saturn.
31. Which planets are called inner planets?
Answer: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
32. Which planets are called outer planets?
Answer: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
33. Write the name of artificial satellite.
Answer: INSAT, IRS, Kalpana-I.
34. What is responsible for the change in season on earth?
Answer: Tilting of earth.
35. Name the planets which have no moon.
Answer: Mercury and Venus.
36. Name the planet where life exists.
Answer: Earth.
37. What is the path on which planets revolve around the sun called?
Answer: Orbit.
38. How many planets are there in the solar system?
Answer: Eight.
39. Name the planet where there is no carbon dioxide.
Answer: Mercury.
Short Answer Type Questions
1: What do you mean by celestial objects. Explain with examples?
Answer: The stars the planets and many other objects in the sky are called celestial objects. For example: moon, nine planets, asteroids etc.
2: Why can’t we hear any kind of sound on moon?
Answer: Moon has no atmosphere and as we know sound cannot travel when there is no medium thus we cannot hear any kind of sound on the moon.
3: Define the following:
(a) Moon
(b) Stars
Answer:
(a) Moon: Moon is a celestial object that does not have its own sunlight; it is visible to us due to reflected sunlight. There is no atmosphere and water on the moon, its surface is dusty and barren. Moon revolves around the earth so it is also called the natural satellite of earth.
(b) Stars: Stars are other celestial object that can be seen in the night sky. Sun is the nearest star from the Earth; the stars are millions of times farther than the sun, STARS are present in the sky during the day time also but because of the bright sunlight they are not visible to us. They appear to move from east to west in the sky.
4: Differentiate between planet and stars.
Answer:
| Planet | Star |
| (i) Have no light of their own. (ii) Do not twinkle. (iii) Most planets on the other hand are near enough to the earth to be magnified by the telescope. (iv) Planets have low temperatures (v) There are only nine planets in the solar system. | (i) Have their own light. (ii) Twinkles at night. (iii) Since the stars are very far away, the telescope can only make them look brighter but not larger (iv) A star has very high temperature. (v) There are billions of stars in the celestial sphere |
5: Differentiate between moon and stars.
Answer: A moon is simply a natural satellite that moves around a planet, tied gravitationally to its parent planet. But a star is a large mass of gas that generates energy due to the thermonuclear fusion reactions happening at their cores. They range in size from a few kilometres in diameter to several times larger than the solar system. They form large collections that make up star clusters and galaxies.
6: Name the person who landed on the moon for the first time along with the date at which he landed there for the first time.
Answer: On July 21, 1969 the American astronaut, Neil Armstrong landed on the moon for the first time.
7: Write some characteristics of stars.
Answer: Some characteristics of stars are as follows:
1. Have their own light.
2. Twinkles at night.
3. Since the stars are very far away, the telescope can only make them look brighter but not larger
4. A star has very high temperature.
5. There are billions of stars in the celestial sphere
8: Why we are not able to see the stars during the day time?
Answer: We are not able to see the stars during the day time because of the bright sunlight.
9: Why stars appear to move from east to west?
Answer: Earth rotates on its axis from west to east, thus stars appear to move from east to west.
10: Define constellation along with some examples.
Answer: Group of stars having a recognisable shape is called constellation. Constellation is an internationally defined area of celestial sphere. For example: Ursa Major, Orion etc.
11: Wright short notes on
(a) Ursa Major
(b) Orion
Answer: Ursa Major: Ursa Major can be seen in the sky during summer time in the early part of the night, it is also known as Big Dipper or Saptarashi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation; it appears like a big question mark or ladle.
Orion: Orion can be seen in the sky during winter in the late evenings. It has seven or eight stars. The brightest star Sirius is located close to the Orion.
12: What is Cassiopeia?
Answer: Cassiopeia: Cassiopeia is a constellation that can be seen in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of night. It looks like distorted letter W or M.
13: Explain why planets do not collide while revolving around the Sun?
Answer: Planets move in their own orbit, thus they do not collide while revolving around sun.
14: What do you mean by satellite? Name some satellites.
Answer: Any celestial body revolving around another celestial body is called its satellite. Aryabhatta, INSAT, IRS, EDUSAT, Kalpana- 1, etc. are some satellites.
15: What are the uses of artificial satellites?
Answer: The artificial planet can communicate with instruments on earth. Artificial satellites have many uses, including relaying communication signals, making accurate surveys and inventories of the earth’s surface and weather patterns, and carrying out scientific experiments.
16: Write short notes on following:
(a) Mercury
(b) Venus
Answer: (a) Mercury: It is the nearest planet to the sun. It is the smallest planet of our solar system. It is very close to the sun so it is quite difficult to observe it. It has no satellite of its own.
(b) Venus: It is the Earth’s nearest planetary neighbour. It is the brightest planet in the night sky. Sometimes it appears in the eastern sky before the sunrise, and sometimes in western sky just after the sunset. Thus it is also called morning or evening star. It has no satellite of its own.
17: Write short notes on the following:
(a) Jupiter
(b) Saturn
Answer: (a) Jupiter: It is the largest planet of the solar system. It rotates very rapidly on its axis. It has a large number of satellites. It also has a faint ring around it.
(b) Saturn: Saturn lies beyond Jupiter; it contains beautiful rings around it which is not visible with the naked eye. It has a large number of satellites. It is least dense among all planets.
18: Define asteroids.
Answer: Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones.
19: Define meteors and meteorites.
Answer: Small pieces of space debris (usually parts of comets or asteroids) that are on a collision course with the Earth are called meteoroids. When meteoroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere they are called meteors. Most meteors burn up in the atmosphere, but if they survive the frictional heating strike the surface of the Earth and they are called meteorites.
20: Explain how you can locate pole star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer: Yes. Pole Star is located by Ursa Major. On a clear moonless sky during summer at 9.00 p.m. at the northern part of sky we can see Ursa Major. Imagine a straight line that passes through these stars and extend this line towards the northern side to a star that is not too bright. This is a Pole Star. This star does not move at all. Ursa Major moves east to west of this Pole Star.
21: Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years?
Answer: Stars are very far from the earth, their distance if written in km will not be convenient to read and memorise, and thus large distances are expressed in light year. It is the distance travelled by light in one year.
22: What do you understand by the statement that the star is six light year away from the earth?
Answer: Stars are millions of kilometres away from the earth. It is not convenient to express such a large distance in the units of km. So the distance of stars from the earth is expressed in time taken by light to travel in one year. Six light years means time taken by light to travel in six years.
23: What are the superstitious about the comets?
Answer: Superstitious about comets is that comets are messengers of disasters, such as wars, epidemics and floods, but it is actually a myth as appearance of comets is a natural phenomenon.
24. What are celestial bodies?
Answer: The stars, the planets, the moon and many other objects in the sky are called celestial bodies.
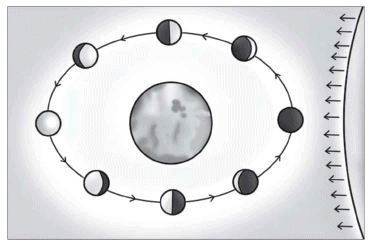
25. Define phases of the moon.
Answer: The various shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called phases of the moon.
26. Why do we see only the part of the moon?
Answer: We see only that part of the moon from which the light of the sun is reflected towards us. So we see only the part of the moon.
27. Why does the size of the moon decrease every day after the full moon day?
Answer: After the full moon day the sunlit part of the moon visible from the earth decreases in size every day.
28. Why do we classify the sun as a star?
Answer: The sun is a star because it has its own source of energy and continuously emits heat and light.
29. Why are stars invisible during the day time?
Answer: Stars are far away from us compared to the sun. So the glare of the sun is much more than the glare of star during the daytime. Therefore, stars are not visible during the day time.
30. What are planets?
Answer: The celestial bodies which revolve around the sun are called planets. There are eight planets in the solar system.
31. Why do stars twinkle but planets not?
Answer: The stars are very far away from the earth. The point position of the stars vibrate to disturbance by air currents and hence they appear to twinkle. The planets are much nearer than of stars and they do not have disturbance by air current, so they do not twinkle.
32. Define orbit.
Answer: A planet has a definite path in which it revolves around the sun. This path is called orbit.
33. What are Asteroids?
Answer: There is a large gap between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. This gap is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the sun. These are called asteroids.
34. What is meteor?
Answer: At night, when the sky is clear and moon is not there, sometimes bright streaks of light may be seen in the sky. This is called meteor.
35. What are meteorites?
Answer: Some meteors are so large that they do not completely evaporate before reaching the earth. These are called meteorites.
36. What is artificial satellite?
Answer: A man made satellite which is orbiting the earth is called artificial satellite.
37. What are comets?
Answer: Comets are the members of our solar system. They revolve around the sun in highly elliptical orbit as a bright head with a long tail.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Differentiate between stars and planets.
Answer:
| Stars | Planets |
| (i) Stars twinkle in the sky. (ii) They are fixed at a point. (iii) They have their own light. (iv) They are very big in size. | (i) Planets do not twinkle in the sky. (ii) They revolve around the sun. (iii) They have no light. (iv) Planets are small as compared to star. |
2. Why can we not hear any sound on the moon?
Answer: Moon is a natural satellite of the earth. It revolves around the earth. But there is no medium on the moon. There is no air on the surface of the moon. Sound travels with the help of any medium. Without the medium it cannot travel from one place to other. So we do not hear any sound on the surface of the moon.
3. What do you know about the phases of the moon? Why do phases of the moon occur?
Answer: The various shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called phases of the moon. The moon does not produce its own light. Whereas the sun and other stars do. We see the moon because the sunlight falling on it is reflected towards us. We therefore see only that part of the moon from which the light of the sun is reflected towards us. The moon revolves around the earth so its position changes every day. The moon appears different at different positions. So the phases of the moon occur.
4. What is the sun? Name the next nearest star. What is the distance of the sun from the earth? Write the unit of the large distances.
Answer: Sun is the nearest star. It also emits light just like the other stars. The next nearest star is Alpha Centauri. The sun is nearly 150 million km away from the earth. Such large distances are expressed in another unit called light year. The distance travelled by light in one year is called light year. The speed of light is about 300000 km per second. Thus the distance of the sun may be said to be about 8 light minutes.
5. What are constellations? Explain some common constellations.
Answer: The group of stars that has a recognizable shape is called constellation.
Some common constellations are:
(i) Ursa Major: It appears during summer time in the early part of the night. It is also known as Big Dipper or Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark.
(ii) Orion: This constellation can be seen during winter in the late evenings. It has seven or eight bright stars. Orion is also called the hunter.
(iii) Cassioplia: It is the most common or prominent constellation in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night. It looks like a distorted letter W or M.
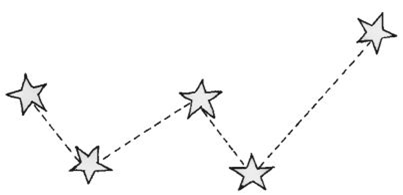
6. What is Pole star? How do you locate the position of Pole star?
Answer: Pole star is the star in the sky which appears stationary and does not move like other stars. It is situated above the north pole of the earth.
Look at the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. Imagine a straight line passing through these stars. Extend this line towards north direction. This line will lead to a star called Pole star.
7. Explain the solar system.
Answer: The sun and the celestial bodies which revolve around it form the solar system. It consists of a large number of bodies such as planets, comets, asteroids and meteors. The gravitational attraction between the sun and these objects keeps them revolving around it. Our earth is also a planet which revolves around the sun. It is also a member of the solar system. There are seven other planets that revolve around the sun. The eight planets are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
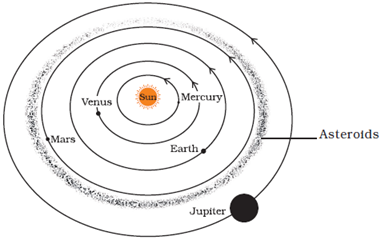
8. Explain the following terms:
(a) Asteroids
(b) Comets
(c) Meteors
(d) Meteorites.
Answer: (a) Asteroids: There is a gap between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This gap is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the sun. These small objects are called asteroids.
(b) Comets: Comets are also small bodies which revolve around the sun in highly elliptical orbits. They become visible from the earth only when they come closer to the sun. They are characterised by a small head followed by a long tail.
(c) Meteors: The very small stone like objects are called meteors. They are commonly known as shooting stars, although they are not stars. The meteor occasionally enters the earth’s atmosphere. Due to friction it heats up. It glows and evaporates quickly.
(d) Meteorites: The portion of meteor which does not burn during its fall through the earth’s atmosphere and hits the ground is called a meteorite.
9. What are planets? Explain them.
Answer: The bodies which revolve around the sun in a certain orbit are called planets. There are following eight planets:
(i) Mercury: The planet Mercury is nearest to the sun. It is the smallest planet of the solar system. It has no satellite of its own.
(ii) Venus: Venus is earth’s nearest planetary neighbour. It is the brightest planet in the night sky. Venus has no moon or satellite of its own.
(iii) Earth: It is the third planet. The earth is the only planet in the solar system on which life exists. Earth appears blue green due to the reflection of light from water and landmass. It has only one moon.
(iv) Mars: The fourth planet is called Mars. It is called the red planet. Mars has two small satellites.
(v) Jupiter: It is the largest planet of the solar system. It is so large that about 1300 earths can be placed inside this giant planet. It has a large number of satellites.
(vi) Saturn: Beyond Jupiter is Saturn, which appears yellowish in colour. It contains beautiful rings which are not visible with naked eyes.
(vii) Uranus: It is the seventh planet. It is the second outermost planet.
(viii) Neptune: The outermost planet is called Neptune.
10: Write short notes on the outermost planet of the solar system.
Answer: Outermost planet of solar system includes planets like Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Jupiter: It is the largest planet of the solar system. It rotates very rapidly on its axis. It has a large number of satellites. It also has a faint ring around it.
Saturn: Saturn lies beyond Jupiter; it contains beautiful rings around it which is not visible with the naked eye. It has a large number of satellites. It is least dense among all planets.
Uranus: It can be seen via telescope only. In its orbital motion it appears to roll on its side. It rotates from west to east.
Neptune: It can be seen via telescope only. Neptune has a planetary ring system, though one much less substantial than that of Saturn.
11: Why phases of the moon occur?
Answer: Just like Earth, half of the moon is lit by the sun, and half is in shadow at any given time. As the moon travels around the Earth, we see the moon from different angles, and thus can see different percentages of light and shadow. When the moon is full, the moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the sun. As a result, we can see the whole of the lit side of the moon. At new moon, exactly the opposite alignment exists, with the moon being between the Earth and the sun. At that point, we can only observe the shadowed side of the moon. At first and third quarter moons, the moon is at a 90 degree angle from the Earth and sun.
12: Differentiate between artificial and natural satellites?
Answer: Natural satellites are celestial body that orbits a planet or any other celestial body, they are found by nature. The most well-known natural satellite is the moon. The natural satellites are made up of natural materials like rocks, minerals, water, dust etc. The natural satellite cannot communicate on earth or with other planets. But artificial satellite is the device placed in orbit around the Earth, moon or other planet. They are man-made. The first artificial satellite was sputnik I. It can communicate with instruments on earth.