Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metal And Non-Metals
Get extra questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metal And Non-Metals with PDF. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts. You can easily download all the questions and answers in PDF format from our app.
Metal And Non-Metals Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers
Question 1: A green layer is gradually formed on a copper plate left exposed to air for a week in a bathroom. What could this green substance be?
Answer: It is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2].
Question 2: A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer: ‘X’ is carbon, ‘Y’ is diamond as it is the hardest natural substance and ‘Z’ is graphite as it is good conductor of electricity.
Question 3: Why does calcium float in water?
Answer: It is because hydrogen gas is formed which sticks to surface of calcium, therefore it floats.
Question 4: Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous. Iodine is a nonmetal which is lustrous,
Answer: Lead is a non-lustrous metal.
Question 5: Which gas is liberated when a metal reacts with an acid? How will you test the presence of this gas?
Answer: Hydrogen gas is formed. Bring a burning matchstick near to it, H2 will burn explosively with ‘pop’ sound.
Question 6: Name the metal which reacts with a very dilute HNOs to evolve hydrogen gas.
Answer: Magnesium
Question 7: Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer: (i) Gold (ii) Silver
Question 8: What is the valency of silicon with atomic number 14?
Answer: Its valency is equal to 4.
Question 9: What is the valency of phosphorus with atomic number 15?
Answer: Phosphorus has valency 3.
Question 10: What is the valency of an element with atomic number 35?
Answer: Its valency is 1.
Question 11: Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity: Na, K, Cu, Ag.
Answer: K > Na > Cu > Ag
Question 12: Write one example of each of
(i) a metal which is so soft that, it can be cut with knife and a non-metal which is the hardest substance.
(ii) a metal and a non-metal which exist as liquid at room temperature.
Answer: (i) Sodium, carbon (diamond).
(ii)Mercury is liquid metal, bromine is liquid non-metal.
Question 13: Mention the names of the metals for the following:
(i) Two metals which are alloyed with iron to make stainless steel.
(ii) Two metals which are used to make jewellary.
Answer:
(i) Nickel and chromium.
(ii) Gold and platinum.
Question 14: Give reason for the following:
(a) School bells are made up of metals.
(b) Electric wires are made up of copper.
Answer: (a) It is because metals are sonorous, i.e. they produce sound when struck with a hard substance.
(b) It-is because copper is good conductor of electricity.
Question 15: Name the following:
(a) A metal, which is preserved in kerosene.
(b) A lustrous coloured non-metal.
(c) A metal, which can melt while kept on palm.
(d) A metal, which is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer: (a) Sodium is preserved in kerosene.
(b) Iodine is lustrous coloured non-metal.
(c) Gallium. ‘
(d) Lead.
Question 16: Explain why calcium metal after reacting with water starts floating on its surface. Write the chemical equation for the reaction. Name one more metal that starts floating after some time when immersed in water.
Answer: Calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of metal.
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2 + H2(g)
Magnesium reacts with hot water and starts floating due to the bubbles of hydrogen gas sticking to its surface.
Question 17: Give reason for the following:
(a) Aluminium oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide.
(b) Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state.
Answer: (a) It is because it reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water. ’Al’ is less electropositive metal. So, it forms amphoteric oxide which can react with acid as well as base.
(b) Ionic compounds can conduct electricity in molten state because ions become free to move in molten state.
Question 18: The way, metals like sodium, magnesium and iron react with air and water is an indication of their relative positions in the ‘reactivity series’. Is this statement true? Justify your answer with examples.
Answer: Yes, sodium reacts explosively even with cold water, it is most reactive. Magnesium reacts with hot water, it is less reactive than Na. Iron reacts only with steam which shows it is least reactive among the three.
Question 19: Out of the two elements, ‘X’ and ‘Y’, which is more reactive and why?
Answer: ‘X’ is more reactive than ‘Y’ because it displaces ‘Y’ from its salt solution.
Question 20: What is an alloy? State the constituents of solder. Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Answer: Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals. One of them can be a non-metal also. Solder consists of lead and tin. It has low melting point which makes it suitable for welding electrical wires.
Question 21: Write chemical equations that shows aluminium oxide reacts with acid as well as base.
Answer: Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Question 22: What is cinnabar? How is metal extracted from cinnabar? Explain briefly.
Answer: Cinnabar is HgS.
Mercury is obtained by roasting cinnabar. HgO formed is thermally unstable and gives mercury.
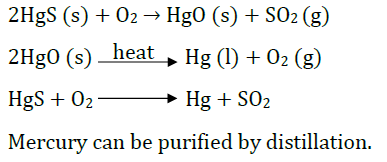
Question 23: (a) Write the electron dot structures for potassium and chlorine.
(b) Show the formation of KCl by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in the compound, KCl.
Answer:
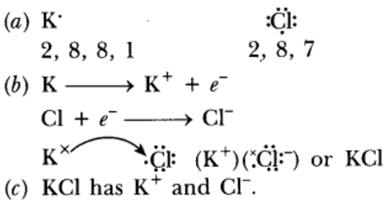
Question 24: (a)State the electron-dot structure for calcium and sulphur.
(b) Show the formation of CaS by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in this compound CaS. Atomic number of Ca = 20, O = 16.
Answer:
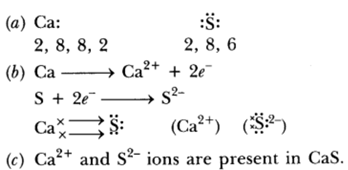
Question 25: You are given samples of three metals. Sodium, magnesium and copper. Suggest any two activities to arrange them in order of decreasing activity.
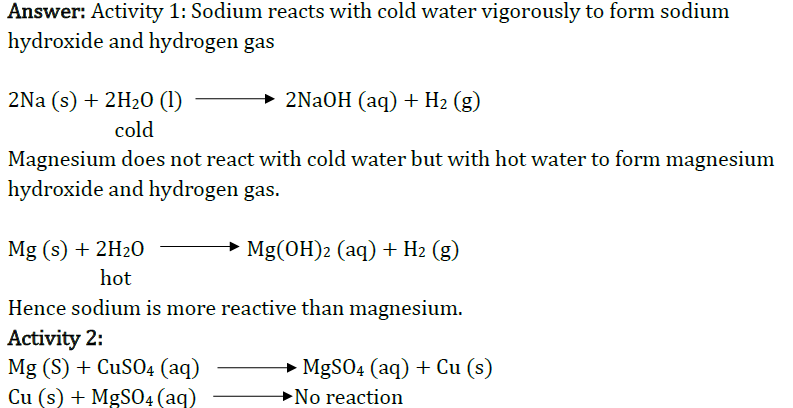
Question 26: Suggest a method of reduction for the following metals during their metallurgical processes:
(i) metal ‘A’ which is one of the last, second or third position in the reactivity.
(ii) metal ‘B’ which gives vigorous reaction even with water and air.
(iii) metal ‘C’ which is kept in the middle df activity series.
Answer: (i) ‘A’ can be obtained by chemical reduction using carbon or carbon monoxide as reducing agent.
(ii) ‘B’ can be obtained by electrolytic reduction.
(iii) ‘C’ can be reduced by reducing agent like ‘Al’.
Question 27: Write balanced equations for the reaction of:
(i) aluminium when heated in air. Write the name of the product.
(ii) iron with steam. Name the product obtained.
(iii) calcium with water. Why does calcium start floating in water?
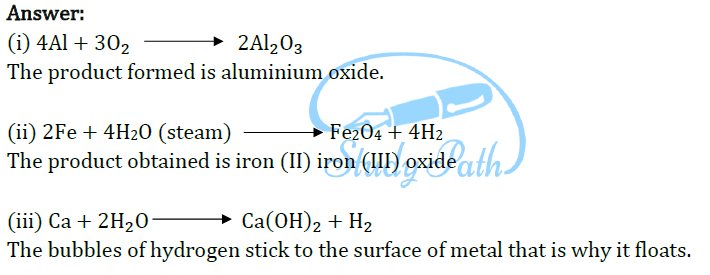
Question 28: Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
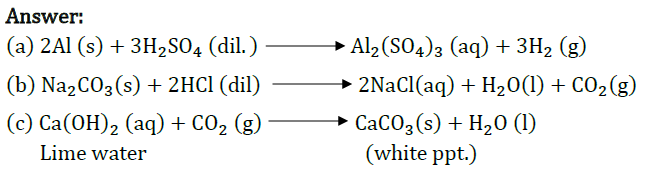
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate.
(c) Carbon dioxide is passed through lime water.
Question 29: (a) Show the formation of Na2O by the transfer of electrons between the combining atoms.
(b) Why are ionic compounds usually hard?
(c) How is it that ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity but they do so when in molten state?
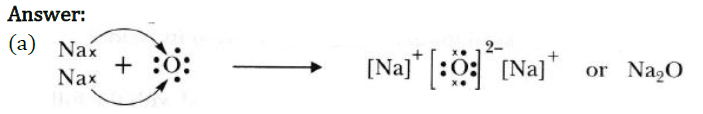
(b) It is due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(c) In solid state, ions are not free to move whereas in molten state ions are free to move, therefore, they conduct electricity in molten state.
Question 30: (a) Show on a diagram the transfer of electrons between the atoms in the formation of MgO. Write symbols of cation and anion present in MgO.
(b) Name the solvent in which ionic compounds are generally soluble.
(c) Why are aqueous solutions of ionic compounds able to conduct electricity?
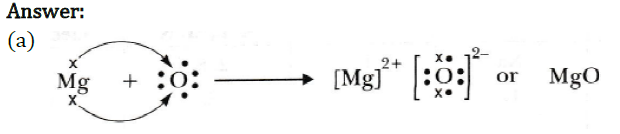
MgO contains Mg2+ as cation and O2– as anion
(b) Ionic compounds are soluble in water.
(c) It is because aqueous solutions consist of ions which can move freely in them and carry current.
Question 31: What are amphoteric oxides? Choose the amphoteric oxides from amongst the following oxides:
Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, CO2, H2O
Answer: Those oxides which reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are called amphoteric oxides, e.g. Na2O, ZnO, are amphoteric oxides among given oxides.
Question 32: Define the terms:
(i) mineral
(ii) ore, and
(iii) gangue.
Answer: (i) Mineral: It is a naturally occurring substance from which metal may or may not be extracted profitably or economically, e.g. Al cannot be extracted profitably from mica.
(ii) Ore: It is a rocky material which contains sufficient quantity of mineral so that metal can be extracted profitably, e.g. zinc blende is an ore of zinc from which zinc can be extracted profitably.
(iii) Gangue: It is a rocky material which is present along with the mineral in the ore, e.g. FeO is gangue in extraction of copper.
Question 33: An ore on heating in air produces sulphur dioxide. Which process would you suggest for its concentration? Describe briefly any two steps involved in the conversion of this concentrated ore into related metal.
Answer: It is concentrated by froth-flotation process.
(i) Roasting: The concentrated sulphide ore is heated strongly in the presence of oxygen to convert it into its oxide.
2ZnS (s) + 3O2 (g) → 2ZnO (s) + 2SO2 (g)
(ii) Reduction: This oxide of metal is reduced with suitable reducing agent to get free metal.
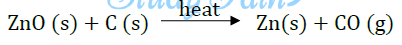
Question 34: Give reasons for the following observations:
(i) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points.
(ii) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating them with carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season.
Answer: (i) Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(ii) It is because these metals themselves are strong reducing agents. Therefore, cannot be reduced by reducing agent like carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels react with CO2, O2 and moisture to form green-coloured basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2].
Question 35: State reasons for the following observations:
(i) The shining surface of some metals becomes dull when exposed to air for a long time.
(ii) Zinc fails to evolve hydrogen gas on reacting with dilute nitric acid.
(iii) Metal sulphides occur mainly in rocks, but metal halides occur mostly in sea and lake waters.
Answer: (i) It is because metal reacts with substances present in atmosphere to form surface compounds which make it dull.
(ii) It is because dil. HNO3 is an oxidising agent therefore zinc gives NO and not H2 with dil. HNO3.
(iii) It is because sea water contains sodium chloride due to which metal halides are formed, whereas sulphur is found below rocks. Therefore, metal – sulphides are formed in rocks.
Question 36: State reasons for the following:
(i) Electric wires are covered with rubber like material.
(ii) From dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc can liberate hydrogen gas but copper cannot.
(iii) Sulphide ore of a metal is first converted to its oxide to extract the metal from it.
Answer: (i) It is because rubber is an insulator and does not allow current to flow through it.
(ii) Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, it can displace hydrogen from dilute HCl whereas copper cannot, because it is less reactive than hydrogen.
(iii) It is because it is easier to reduce oxide ore as compared to sulphide ore.
Question 37: (a) Write electron dot diagram for chlorine (At No. 17) and calcium (At No. 20). Show the formation of calcium chloride by transfer of electrons.
(b) Identify the nature of above compound and explain three physical properties of such compound.
Answer:
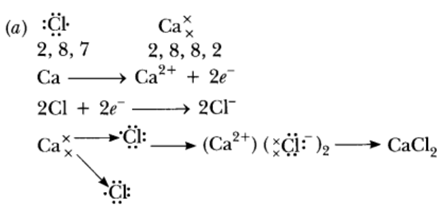
(b) It is ionic compound.
Physical properties
- 1.It is hard and solid.
- 2.It has high melting and boiling point.
- 3.It soluble in water.
Question 38: (a) An ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervesces. What type of ore is this? What steps will be required to obtain metal from the enriched ore.
(b) Copper coin is kept immersed in silver nitrate solution for some time. What change will take place in coin and colour of the solution? Write balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: (a) Carbonate ore:
(i) Calcination: Carbonate ore is heated in limited supply of air and oxide is obtained,
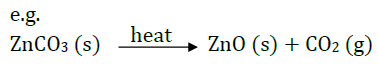
(ii) Reaction with carbon: Oxide ore is heated with carbon
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
(b) Copper, being more reactive than silver will displace silver from silver nitrate solution and there will be deposition of silver on copper coin. The colour of solution will turn to blue.
Cu (s) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (S)
Question 39: (a) Define activity series of metals. Arrange the metals gold, copper, iron and magnesium in order of their increase in reactivity.
(b) What will you observe when:
(i) Some zinc pieces are put in copper sulphate solution.
(ii) Some silver pieces are put into green coloured ferrous sulphate solution.
Answer: (a) The series of metals in which metals are arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity. Au < Cu < Fe < Mg is increasing order of reactivity.
(b) (i) The blue solution will become colourless and reddish brown copper metal will be deposited.
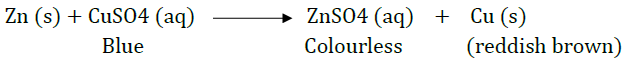
(ii) Ag (s) + FeSO4 (aq) → No reaction
Reaction will not take place because ‘Ag’ is less reactive than iron.
Question 40: (a) Write the chemical name of the coating that forms on silver and copper articles when these are left exposed to moist air.
(b) Explain what is galvanisation. What purpose is served by it?
(c) Define an alloy. How are alloys prepared? How do the properties of iron change when:
(i) small quantity of carbon,
(ii) nickel and chromium are mixed with it.
Answer: (a) Ag2S (silver sulphide) is formed on silver, basic copper carbonate CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 is formed on copper.
(b) The process of coating zinc over iron is called galvanisation. It is used to prevent rusting of iron.
(c) Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals. One of them can be non-metal. Alloys are prepared by melting two or more metals together.
(i) Iron does not rust on adding small quantity of carbon.
(ii) When we form alloy of iron with nickel and chromium, we get stainless steel which is malleable and does not get rusted.
Question 41: (a) In the formation of a compound between two atoms A and B, A loses two electrons and B gains one electron.(i) What is the nature of the bond between A and B?
(ii) Suggest the formula of the compound formed between A and B.
(b) On similar lines explain the formation of MgCl2 molecule.
(c) Common salt conducts electricity only in the molten state. Why?
(d) Why is the melting point of NaCl high?
Answer:
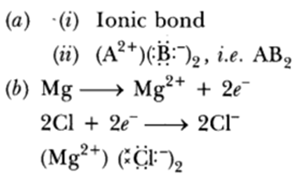
(c) Na+ and Cl— are free to move in molten state but not in solid state.
(d) It is due to strong force o attraction between Na+ and Cl—.
Question 42: (a) Carbon cannot be used as reducing agent to obtain Mg from MgO. Why?
(b) How is sodium obtained from molten sodium chloride? Give equation of the reactions.
(c) How is copper obtained from its sulphide ore? Give equations of the reactions.
Answer: (a) It is because ‘Mg’ is stronger reducing agent than carbon.
(b) Sodium is obtained from molten NaCl by electrolysis.
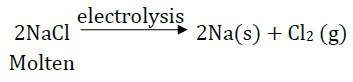
c) Copper ore is concentrated by froth-flotation process.
Roasting: 2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
Bassemerisation: Copper oxide reacts with Cu2S on heating to form Blister copper and SO2.
Cu2S + 2Cu2O → 6Cu + 2SO2
Blister Copper is purified by electrolytic refining.
Question 43: How is the method of extraction of metals high up in the reactivity series different from that for metals in the middle? Why the same process cannot be applied for them? Explain giving equations, the extraction of sodium.
Answer: Metals high up in the series are obtained by electrolytic reduction because these metals are strong reducing agents and therefore, cannot be obtained by chemical reduction.
Metals in middle of series are less reactive and can be obtained by chemical reduction. The same process cannot be used for both of them as highly reactive metals cannot be obtained by chemical reduction.
Extraction of sodium is done by electrolysis of molten sodium chloride.
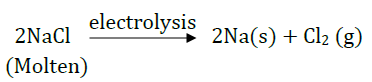
Question 44: Write the names and symbols of two most reactive metals. Explain by drawing electronic structure how any one of the two metals react with a halogen. State any four physical properties of the compound formed.
Answer: K(Potassium) and Na(Sodium) are the two most reactive metals. K and Na are electronic structures as they have one valence electron.
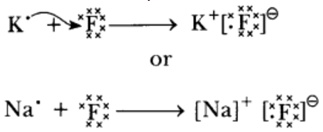
where ‘F’ is a halogen.
Four physical properties of the compounds formed by these elements and halogens are:
(i) They have high melting point.
(ii)They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state not in solid state.
(iv) They are solid and somewhat hard.
Question 45: Give reasons for the following:
(i) Silver and copper lose their shine when they are exposed to air. Name the substance formed on their surface in each case.
(ii) Tarnished copper vessels are cleaned with tamarind juice.
(iii) Aluminium is more reactive than iron yet there is less corrosion of aluminium as compared to iron when both are exposed to air.
Answer: (i) These metals get corroded. Silver forms black Ag2S (silver sulphide) and copper form greenish layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3.Cu(OH)2.
(ii) Tamarind contains acid which reacts with basic copper carbonate and product gets dissolved and removed from copper vessel.
(iii) Aluminium forms oxide layer on its surface which does not further react with air.
Question 46: (a) Write the electron dot structures of sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(b) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by transfer of electrons. Name the ions present in these compounds.
(c) List three properties of ionic compounds.
Answer:
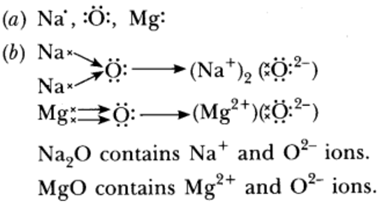
(c) (i) They are solids having high melting point.
(ii) They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
Question 47: What are alloys? How are they made? Name the constituents and uses of brass, bronze and solder.
Answer: Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals. One of them can be a non-metal also. They are made by melting a metal which is in large amount first and then adding the other metal.
Brass contains copper and zinc. It is used for making decorative articles. Bronze contains copper and tin. It is used for making statues and medals. Solder contains lead and tin. It is used for soldering purposes.
Question 48: A metal (E) is stored under kerosene. When a small piece of it is left open in the air, it catches fire. When the product formed is dissolved in water, it turns red litmus to blue.
(i) Name the metal (E).
(ii)Write the chemical equation for the reaction when it is exposed to air and when the product is dissolved in water.
(iii) Explain the process by which the metal is obtained from its molten chloride.
Answer: (i) ‘E’ is sodium which catches fire in presence of moisture.
(ii) 4Na + O2 → 2Na2O
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
(iii) Electrolytic reduction: Electric current is passed through molten NaCl. Sodium is formed at cathode and chlorine gas is liberated at anode.
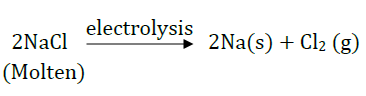
Question 49: Write two differences between calcination and roasting.
Answer:
| Calcination | Roasting |
| Calcination is a process in which ore is heated in the absence of air or air might be supplied in limited quantity | Roasting involves heating of ore lower than its melting point in the presence of air or oxygen. |
| Calcination involves thermal decomposition of carbonate ores. | Roasting is carried out mostly for sulphide minerals. |
| During calcination, moisture is driven out from an ore. | Roasting does not involve dehydrating an ore. |
| Carbon dioxide is given out during calcination | During roasting large amount of toxic, metallic and acidic compounds are released. |
Question 50: (a) Name the main ore of mercury. How is mercury obtained from its ore? Give balanced chemical equation.
(b) What is thermite reaction? How is it used to join the railway tracks or cracked machine parts?
(c) Name the method used to extract metals of high reactivity.
Answer: (a) Cinnabar
Mercury is obtained from its ore by roasting.
HgS + O2 → Hg + SO2
(b) When aluminium is heated with Fe2O3 to get molten iron, it is called thermite reaction.
Fe2SO3 + 3Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
Molten iron is used to weld broken railway tracks.
(c) Electrolytic reduction
Question 51: (a) How can the metals at the top of the reactivity series be extracted from their ores? Explain with an example.
(b) Name any one alloy made from
(i) a metal and a non-metal, and
(ii) two metals.
Answer: (a) These metals are extracted by electrolytic reduction, e.g. aluminium is obtained from bauxite by electrolytic reduction.
(b) (i) Steel is made up of iron and carbon.
(ii) Brass is made up of copper and zinc.
Question 52: With the help of a suitable example, explain how ionic compounds are formed. State any three general properties of ionic compounds.
Answer: Ionic compounds are formed by transfer of electrons from metal to non-metals, e.g.
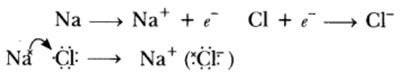
General Properties:
(i) They are the solids having high melting point.
(ii) They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
Question 53: (a) Explain with an example how the metal (X) which is low in reactivity series and metal (Y) which is high in the reactivity series are obtained from their compounds by reduction process.
(b) Write the electronic configurations of sodium and chlorine. Show the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine by the transfer of electrons.
(c) List any two observations when a highly reactive metal is dropped in water.
Answer: (a) ‘X’ is obtained by chemical reduction. ‘Y’ is obtained by electrolytic reduction.
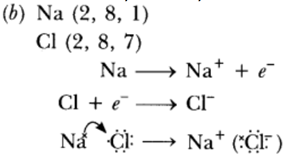
(c) (i) Metal will catch fire.
(ii) Alkali solution is formed which turns red litmus blue.
Question 54: (a) The reaction of metal (X) with ferric oxide is highly exothermic. Metal
(X) is obtained from its oxides by electrolytic reduction. Identify (X) and write its reaction with ferric oxide.
(b) Give reason to justify that aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide. Also, give another example of amphoteric oxide.
(c) Mention constituent metals present in bronze.
Answer: (a) ‘X’ is ‘Al’
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe
(b) AI2O3 reacts with acid as well as base therefore it is amphoteric oxide.
AI2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
AI2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
Zinc oxide is also an amphoteric oxide.
(c) Bronze contains’ copper and tin.