CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 6 Changes Around Us are given below. Our notes are designed by the subject experts and are as per the NCERT guidelines. These notes include all the important points of the chapter in detailed way, so you can refer to this whenever required. Study Path provides CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 6 that are easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format, so students can practice it for their studies and get good marks in their examinations.
Changes Around Us Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 6
Every day we come across different types of changes. Turning day into night, night into a day, rising and setting of sun and moon, changing of climate, melting of ice, and lot more. These changes occur in a minute or may take a longer time. Few changes are not even noticeable.
On this basis, changes around us can be classified into two broad categories:
Change
- Any difference in the size or shape of an object is referred to as a change.
- Changes are either reversible or irreversible.
Reversible change
- Reversible change is that change that can be reversed by one or more methods.
- Usually, there is a change in physical properties, shape and size of the material.
- Mostly a new substance is not formed in a reversible change. For eg: folding of paper, elongation of spring etc.
Irreversible change
- The change, which is permanent and cannot be undone by any physical or chemical means is called an irreversible change.
- Formation of new substance is involved in this change.
- For example, the burning of a candle is an irreversible change as we cannot get back the candle once burnt.
Substances and materials usually undergo two major types of changes:
Physical change: This represents a change not in the chemical identity but the physical form of a substance. When substances undergo a physical change, there is no formation of a new substance and more or less these changes can be reversed. Example: boiling of water and melting of ice represent reversible physical changes while growing of height is an irreversible physical change.
Chemical change: This represents a change in the chemical identity of a substance. These are irreversible changes because the original substance gets converted into a new substance and cannot be brought back. Example: cooking of rice, burning of matchstick etc.
Difference between physical and chemical changes:
| Physical Change | Chemical Change |
| A change in matter which occurs without causing any change in the composition of the matter is known as physical change | While a chemical change is defined as the change in the chemical composition of matter |
| Usually, physical changes are reversible in nature | While chemical changes are often irreversible |
| No new products are formed when an object undergoes physical change | Chemical changes often lead to formation of new products |
| These changes have no impact on the molecular composition of the substance | Chemical changes have a direct impact on the chemical bonds and molecular composition of a substance |
| A few changes occur when cooling or heating is done | These changes involve absorption or release of energy |
There are other ways to bring about changes in substances:
Mixing two substances together: A small amount of curd is added to warm milk which leads to conversion of that milk into curd. This is an irreversible change.
When we add a salt to water it becomes salty but this is a reversible change.
Expansion and Contraction: In order to make tools like an axe, the ring of its iron blade is heated which allows it to expand i.e., become larger in size and then is allowed to cool down which makes it contract again i.e., become smaller in size leading to a tight fit of the handle.
Expansion and Contraction
- When the temperature increases, the particle of a substance expands or becomes loose. When this happens, the material is said to undergo expansion.
- When the temperature decreases, the particles of substance contracts or becomes tight. When this happens, the material is said to undergo contraction.
- The amount of expansion or contraction varies in solids, liquids and gases.
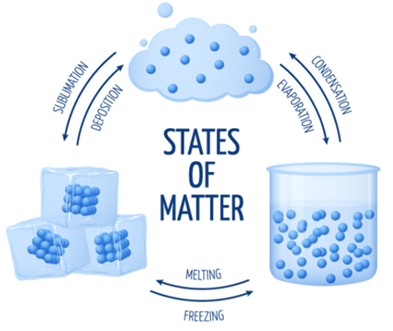
- There are physical changes that take place when a substance or material moves from one state of matter to another.
- Water is a classic example as it can exist as either solid, liquid or gas.
- Water at very low temperatures exists as a solid known as ice. On applying heat or increasing the temperature, the ice ‘melts’ to form water. The physical change when a solid changes to liquid is called melting.
- If we keep increasing the temperature, the water now starts to boil until it fully becomes water vapour. The physical change when a liquid changes to gas is called evaporation.
- To get back the water from water vapour, it is possible by condensation – a physical change where the gas changes to a liquid. This is possible by lowering the temperature.
Anomalous expansion of water
Water on cooling contracts up to 4°C. On further cooling, up to 0°C, water expands rather than contracting with decrease in temperature. This means that as the temperature decreases from 4°C to 0°C, water expands. This behaviour is called anomalous expansion of water.
Burning: Burning is an irreversible change where a substance burns to produce new material. These new materials are ash and some gases.
For example. paper is burnt to produce ash, which is different from paper in terms of appearance and properties.
Separation
The separation of the components of a mixture or an impure substance are carried out with the following purposes:
- To remove the unuseful or harmful component.
- To obtain the useful component.
- To remove impurities for getting a pure sample.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 14 – Free PDF Download
Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by clicking on the chapter names provided above.