CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 Body Movements
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 Body Movements are given below. Our notes are designed by the subject experts and are as per the NCERT guidelines. These notes include all the important points of the chapter in detailed way, so you can refer to this whenever required. Study Path provides CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 that are easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format, so students can practice it for their studies and get good marks in their examinations.
Body Movements Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 8
Introduction
Our body is capable of performing a wide variety of simple and complex functions. It is able to do so because of the internal structure that facilitates its movement.
Movements
The ability of organisms to change position, by using their body parts, is called movement.
Human Body and Its Movements
The human skeleton is the internal framework which is responsible for giving support, shape and protection to our bodies. It contains 206 bones, each playing a distinct yet important task. The skeleton can be classified into two parts called as the axial and the appendicular. The axial skeleton comprises of the central part of the skull, spine, and ribs and the appendicular skeleton consists of the arms and legs.
Limbs: The arms or legs of an animal.
Bones: These are the hard white structures below our skin that protect our internal organs. Bones are incapable of bending.
Joints: These are defined as the points at which two bones are fitted together. These are the points at which we can rotate and bend our bodies.
Skeletal System
Skeleton
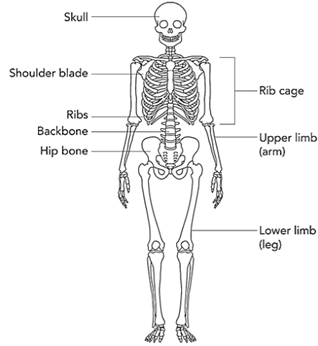
- Skeleton is the internal structure in organisms, which helps in bringing about movement.
- It forms a framework that gives the shape of the body and provides support to organisms.
- The skeleton is made up of bones.
- Different kinds of bones are joined to each other in a particular manner.
- These joints facilitate various types of movements.
- In higher animals, bones, muscles and cartilage together make the movement possible.
Important Points to remember in a Human Skeleton:
- Bones provide support, protection, movement and perform several other functions.
- The bones in the skull (Cranium, Mandible, Maxilla) give protection to the brain.
- The long bones such as humerus, radius, ulna, tibia, fibula support the weight of body
- The carpals are located in wrist and tarsals are located in ankles. They are examples of short bones.
- The bones protecting the spine are called as the vertebral column. Cervical area (top 7 vertebrae), Thoracic (next 12), Lumbar (bottom 5 vertebrae), Sacrum (5 fused or stuck together bones) and Coccyx (the tiny bit at the bottom of the spine).
- The sternum and rib cage constitute the chest bones.
Muscles
- Muscles are parts of the body that help in bringing about movement.
- Muscles may be attached to bones, (humans) or may work alone (earthworm).
Cartilage
- Part of the skeleton that is not hard as bones and can be bent, is cartilage.
- They are found in the upper part of the ear, the tip of the nose and at the tips of long bones.
Joints
- Joints are the points where two parts of the skeleton are fitted together to make movement possible.
- Examples are hip joint, elbow joint, knee joint, etc
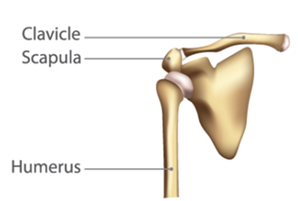
Ball and Socket Joint
- Ball and socket joint, where the rounded end of one bone fits into the cavity of the other bone.
- It brings in movement in all directions.
- It is seen in the hips and shoulders of the human body.
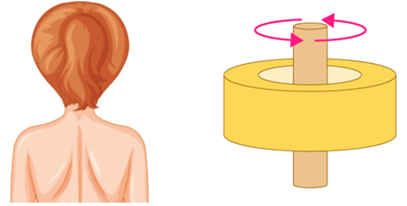
Pivot Joint
- A pivotal joint is where a cylindrical bone rotates in a ring.
- It joins the neck to the head.
- It allows to bend the head forward and backwards and turn the head to our left or right.
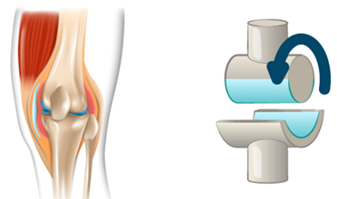
Hinge Joints
- Hinge joints bring about movement in only back and forth direction.
- The knees and elbows have hinge joints.
- The following image is a hinge joint in the elbow.
Fixed Joints
- Fixed joints are immovable joints because the bones are joined together.
- Such joints are found in the skull.
Gaits of Animals
The different patterns of movement of animals due to the differences in their skeletal structure are called gaits of animals.
Earthworm
- The earthworm does not have any internal skeleton.
- The body is made up of many rings joined end to end and muscles attached to these rings help to extend and shorten the body.
- The skin of earthworm also has a large number of tiny bristles that help it get a good grip on the ground.
- Repeated extension and contraction of the body muscles, enable the earthworm to move through the soil.
Snail
- Snails move with the help of their muscular, flat foot.
- They glide along a solid surface which is lubricated with mucus.
- This motion is powered by succeeding waves of muscular contractions of the foot.
Cockroach
- The body of a cockroach is covered with a hard outer skeleton that is made of different units joined together.
- It has three pairs of legs for walking and two pairs of wings attached to the breast for flying.
- It has distinct muscles that are used for movement.
- The muscles attached to the legs help in walking.
- The breast muscles attached to the wings help in flying, although they are not good flyers.
Birds
- Birds have a special skeletal and muscular structures that help them to fly.
- The forelimbs are modified to become wings and the bones inside are hollow to suit flying.
- The bones of the hind limbs are used for perching and walking.
- The shoulder bones and breastbones are strong and support muscles of flight, which move the wings up and down.
Fish
- Fishes have a streamlined body that helps them swim with least resistance.
- They use tail fin for small jerks through water and other fins assist swimming.
- The tail fin is also used for changing directions.
Snakes
- Snakes do not have legs for movement but use their long backbone along with muscles for movement.
- Their body curves into many loops, which gives it a forward push by pressing against the ground.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 – Free PDF Download
Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by clicking on the chapter names provided above.