Light Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Light Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Extra Questions with Answers are provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light Extra Questions
Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1: Name a device which works on the reflection of reflected light.
Answer: Periscope
Question 2: Name the point inside the human eye where no vision is possible.
Answer: Blind spot
Question 3: Name an eye disease caused by the deficiency of vitamin A in the diet.
Answer: Night blindness
Question 4: What type of reflection of light takes place from a plane mirror?
Answer: Regular reflection
Question 5: Which part of the eye converges light rays to form the image?
Answer: Eye lens
Question 6: Where is the image of an object formed in human eye?
Answer: Retina
Question 7: Which part of the eye carries images to the brain?
Answer: Optic nerve carries images to the brain.
Question 8: How many mirrors are there in a periscope?
Answer: The periscope makes use of two plane mirrors.
Question 9: Name an instrument or toy which works by producing multiple reflections from three plane mirrors to form beautiful patterns.
Answer: Kaleidoscope
Question 10: How many images of a candle will be seen when two mirrors are set parallel to each other and a candle is placed between them?
Answer: Infinite number of images of the candle will be formed.
Question 11: What type of reflection of light takes place from a rough surface?
Answer: The diffuse reflection of light takes place from a rough surface.
Question 12: What type of reflection of light takes place from a smooth surface?
Answer: Regular reflection of light takes place from a smooth surface.
Question 13: Which type of reflection of light leads to the formation of images?
Answer: Images are formed by regular reflection.
Question 14: What is an ‘incident ray’?
Answer: The light ray, which strikes any surface, is called the incident ray.
Question 15: What kind of lens (convex or concave) is there in our eyes?
Answer: The human eye has convex lens.
Question 16: What are the main parts of the human eye?
Answer: Important parts of the eye are cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina and optic nerve.
Question 17: What is angle of incidence?
Answer: The angle between the normal and incident ray is called the angle of incidence (∠i).
Question 18: What do you mean by ‘point of incidence’?
Answer: The point of incidence is the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror.
Question 19: How we see the moon?
Answer: Moon receives light from the sun and reflects it. That’s how we see the moon.
Question 20: What are the two types of reflection of light?
Answer: The two types of reflection of light are Regular reflection of light and Diffused reflection of light.
Question 21: What is a ‘ reflected ray’?
Answer: The ray that comes back from the surface after reflection is known as the reflected ray.
Question 22: What is angle of reflection?
Answer: The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is known as the angle of reflection (∠r).
Question 23: What are the uses of periscope?
Answer: Periscopes are used in submarines, tanks and also by soldiers in bunkers to see things outside.
Question 24: Write the uses of kaleidoscope.
Answer: Designers of wallpapers and fabrics and artists use kaleidoscopes to get ideas for new patterns.
Question 25: What is the most comfortable distance at which one can read with a normal eye?
Answer: The most comfortable distance at which one can read with a normal eye is about 25 cm.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What are luminous objects? Give some examples.
Answer: The objects which emit their own light are known as luminous objects. Example: sun, fire, flame of a candle and an electric lamp.
Question 2: What are illuminated objects? Give one example.
Answer: The objects which shine in the light of other objects are called illuminated objects. Example: moon.
Question 3: Why cannot we see a book which is placed behind a wooden screen?
Answer: Wooden screen are opaque object that does not allow light to pass through it. Thus, we are not able to see through it.
Question 4: What is blind spot in the eye?
Answer: At the junction of the optic nerve and the retina, there are no sensory cells, so no vision is possible at that spot. This is called the blind spot.
Question 5: What type of image is formed by a plane mirror?
Answer: The image formed by a plane mirror is always virtual, upright, and of the same shape and size as the object it is reflecting.
Question 6: What is lateral inversion?
Answer: In an image formed by a mirror the left of the object appears on the right and the right appears on the left. This is known as lateral inversion.
Question 7: What is meant by dispersion of light’? Name a natural phenomenon showing dispersion.
Answer: Splitting of light into its colours is known as dispersion of light. Rainbow is a natural phenomenon showing dispersion.
Question 8: A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of 40°. What is the angle of reflection?
Answer: The angle of reflection will be 40 degree. This is by the law of reflection that angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Question 9: Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teachers advise?
Answer: Laser light is harmful for the human eye because it can injure the retina. Hence, it is advisable not to look at a laser beam directly.
Question 10: Which part of the eye gives it its distinctive color?
Answer: The iris is the part of that eye which gives it its distinctive colour. When we say that a person has green eyes, we refer actually to the colour of the iris.
Question 11: What happens to the size of the pupil of our eye in bright light?
Answer: In bright light the size of the pupil of our eye becomes small to reduce the amount of light going inside the eye. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris.
Question 12: How can you show that white light consists of seven colors?
Answer: White light consists of seven colors can be shown by passing the light through a prism. The sunlight passes through the prism and splits into a band of 7 colors.
Question 13: What makes things visible?
Answer: Eyes alone cannot see any object. It is only when light from an object enters our eyes that we see the object. The light may have been emitted by the object, or may have been reflected by it.
Question 14: What is ‘normal’ in the reflection of light from a plane mirror?
Answer: A line drawn making an angle of 90º to the line representing the mirror at the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror is known as the normal to the reflecting surface at that point.
Question 15: What is the name of transparent front part of an eye?
Answer: The eye has a roughly spherical shape. Outer coat of the eye is white. It is tough so that it can protect the interior of the eye from accidents. Its transparent front part is called cornea.
Question 16: Name some food items which are rich in vitamin A.
Answer: Raw carrots, broccoli and green vegetables (such as spinach) and cod liver oil are rich in vitamin A. Eggs, milk, curd, cheese, butter and fruits such as papaya and mango are also rich in vitamin A.
Question 17: Why too little or too much light is bad for our eyes?
Answer: Too little or too much light is bad for eyes. Insufficient light causes eyestrain and headaches. Too much light, like that of the sun, a powerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina.
Question 18: A book lying on a table in a room can be seen from all the parts of the room. Give reason?
Answer: A book lying on a table in a room can be seen from all the parts of the room because the light is reflected by the book and it reaches our eye at any part of the room.
Question 19: What should we do if something like a dust particle or an insect gets into our eye?
Answer: If something like a dust particle or an insect gets into our eye, we should never rub the eye instead wash the eye with clean water. If there is no improvement, we should consult a doctor immediately.
Question 20: How a hair dresser makes us see hair at the back of our head after the hair cut is complete?
Answer: Hair dresser uses the phenomena of multiple reflections to provide view of the back of our head. After our hair cut is complete, he places a mirror at our back to show us how the hair has been cut.
Question 21: State the laws of reflection.
Answer: Two laws of reflection are:
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) Incident ray, reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface, lie in the same plane.
Question 22: How do we see a moving picture or a movie?
Answer: movies that we see are actually a number of separate pictures in proper sequence. They are made to move across the eye usually at the rate of 24 pictures per second (faster than 16 per second). So, we see a moving picture.
Question 23: What are rods and cones in the retina of an eye?
Answer: There are two kinds of light sensitive cells on the retina.
(i) cones, which are sensitive to bright light and
(ii) rods, which are sensitive to dim light.
Besides, cones sense colour.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What happens when a ray of light falls perpendicularly on the surface of a plane mirror?
Answer: The angle of incidence for such a ray of light is zero. Since the angle of incidence is zero, so according to the law of reflection, the angle of reflection should also be zero. This means that the reflected ray will also travel back from the mirror along the normal.
Question 2: How many images of the coin will be seen when two plane mirrors are set at right angles to each other and a coin is placed in-between these two plane mirrors?
Answer: The formula to calculate the no. of images of an object placed between 2 plane mirrors is (360°/x°)−1; where ‘x’ is the angle of inclination.
(360°/90°)−No. of images formed
= (360°/90°)−1
= 4−1
=3
Question 3: What is cataract? How can the vision of a person having cataract be restored?
Answer: Sometimes, particularly in old age, eyesight becomes foggy. It is due to the eye lens becoming cloudy. When it happens, persons are said to have cataract. There is a loss of vision, sometimes extremely severe. It is possible to treat this defect. The opaque lens is removed and a new artificial lens is inserted. Modern technology has made this procedure simpler and safer.
Question 4: Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
Answer: If we are in dark room, then it is not possible for us to see the objects in the room. However objects outside the room are visible to us. This is so, because eyes alone cannot see any object. It is only when light from an object enters our eyes that we see the object. The light may have been emitted by the object, or may have been reflected by it.
Question 5: How does eye adjust itself to deal with light of varying intensity?
Answer: The iris controls the amount of light entering into the eye by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil according to the intensity of the light that the eye receives. If the amount of light is high, the iris contracts the pupil and reduces the amount of light entering the eyes. If the amount of light is less, the iris expands the pupil so that more light can enter the eye and the things can be viewed clearly.
Question 6: Explain why, an owl can see well in the night but not during the day whereas an eagle can see well during day but not in the night.
Answer: A night bird (owl) can see very well in the night but not during the day. On the other hand, day light birds (kite, eagle) can see well during the day but not in the night. The Owl has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light in its eye. Also, it has on its retina a large number of rods and only a few cones. The day birds on the other hand, have more cones and fewer rods.
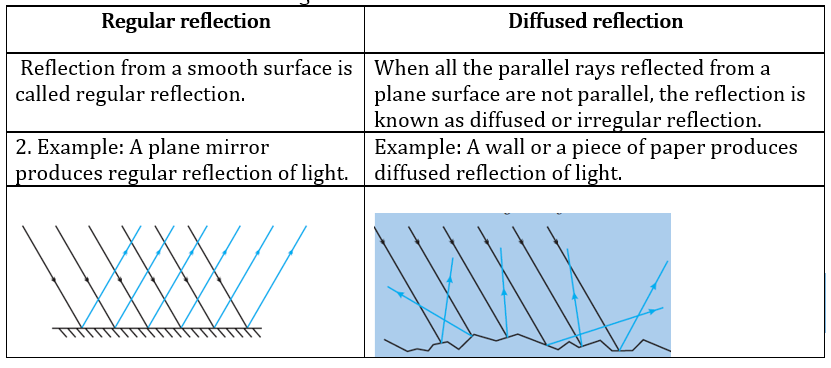
Question 7: Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer: Difference between regular and diffused reflection
Question 8: What are the functions of the following parts of the eye?
Iris, Eye-lens, Retina and Optic nerve
Answer:
- Iris – Iris controls the size of the pupil. The iris is the part of that eye which gives it its distinctive colour.
- Eye-lens – The lens focuses light on the back of the eye, on a layer called retina.
- Retina – Retina receives the light focused by the lens. Retina contains several nerve cells. Sensations felt by the nerve cells are then transmitted to the brain.
- Optic nerve – The job of the optic nerve is to transfer visual information from the retina to the brain.
Question 9: Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Answer: It is necessary that we take proper care of our eyes. If there is any problem we should go to an eye specialist. Have a regular checkup.
- If advised, we should use suitable spectacles.
- Too little or too much light is bad for our eyes. Insufficient light causes eyestrain and headaches. Too much light, like that of the sun, a powerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina.
- We should not look at the sun or a powerful light directly.
- We should not rub our eyes. If something gets into the eyes, we should splash the eyes with a lot of clean water. If there is no improvement then we should consult a doctor.
- We should wash our eyes frequently with clean water.
- We should always read at the normal distance for vision. We should not read by bringing our book too close to our eyes or keeping it too far.
At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.