Combustion and Flame Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Combustion and Flame Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions and Answers are provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Extra Questions
Very Short Type Question
Question 1: Name some of the substances which burn without producing a flame.
Answer: Coal and Charcoal
Question 2: Name two substances having low ignition temperature.
Answer: paper and white phosphorus
Question 3: Name two substances having high ignition temperature.
Answer: coal and log of wood
Question 4: Name some common fuels.
Answer: wood, charcoal, petrol and kerosene
Question 5: Name some solid fuels.
Answer: wood, charcoal, coal, coke and cow-dung cakes
Question 6: Name some liquid fuels.
Answer: kerosene, petrol and diesel
Question 7: Name some gaseous fuels.
Answer: natural gas, petroleum gas, biogas and coal gas
Question 8: Which is the most common fire extinguisher?
Answer: The most common fire extinguisher is water.
Question 9: Name one substance which burn in air at room temperature?
Answer: Phosphorus burns in air at room temperature.
Question 10: How are heat and light produced in the sun?
Answer: In the sun, heat and light are produced by nuclear reactions.
Question 11: Name the term which is used to express the efficiency of a fuel.
Answer: The term Calorific value is used to express the efficiency of a fuel.
Question 12: Describe one method of putting out a fire caused by burning wood or paper.
Or
How will you put out a fire caused by burning wood or paper?
Answer: Water can be used when things like wood and paper are on fire.
Question 13: Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answer: The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Question 14: What is global warming?
Answer: Global warming is the rise in temperature of the atmosphere of the earth.
Question 15:What is fuel?
Answer: The substance that undergoes combustion is said to be combustible. It is also called a fuel.
Question 16: Which gas is produced due to incomplete combustion of fuel?
Answer: Incomplete combustion of fuels produces a very poisonous gas called carbon monoxide.
Question 17: Name the fuel which is gradually replacing petrol and diesel in automobiles.
Answer: The use of diesel and petrol as fuels in automobiles is being replaced by CNG (Compressed Natural Gas).
Question 18: What is ignition temperature?
Or
What is the ignition temperature of a substance?
Answer: The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
Question 19: What is meant by the calorific value of a fuel?
Answer: The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What are the three zones of flame?
Answer: There are three different zones of a flame – innermost zone (dark zone), middle zone (luminous zone) and outer zone non-luminous zone.
Question 2: What is combustion? Give example.
Answer: A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat is called combustion. Example: Burning of charcoal.
Question 3: Why food is called fuel for our body?
Answer: Food is called fuel for our body because in our body food is broken down by reaction with oxygen and heat is produced.
Question 4: Why is the innermost zone of a flame black in colour?
Answer: The innermost zone of a flame is black in colour due to presence of unburnt vapours of the combustible material.
Question 5: Explain how CO2 is able to control fires.
Answer: CO2, being heavier than oxygen, covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled.
Question 6: Which is the best fire extinguisher for fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol?
Answer: For fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher.
Question 7: Why is water not used to control fires involving electrical equipment?
Or
Explain why fire caused by electricity should not be extinguished by pouring water?
Or
Why water is not suitable for extinguishing fire caused due to electrical appliances?
Or
Why can we not use water to extinguish fire caused due to electrical appliances?
Answer: Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment because water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire.
Question 8: What are the harmful products released by the burning of fuels?
Answer: The harmful products released by the burning of fuels are unburnt carbon particles, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides etc.
Question 9: What is rapid combustion? Give one example.
Answer: The combustion that takes place rapidly and produces heat and light is called rapid combustion. Example: Gas burns rapidly and produces heat and light.
Question 10: Why are fires produced by burning oil not extinguished by pouring water?
Or
Water is not suitable for fires involving oil and petrol. Explain.
Or
The fire produced by petrol cannot be extinguished by using water. Explain why?
Answer: Water is heavier than oil. So, it sinks below the oil, and oil keeps burning on top. Thus, water is also not suitable for fires involving oil and petrol.
Question 11: What causes global warming?
Answer: Combustion of most fuels releases carbon dioxide in the environment. Increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is believed to cause global warming.
Question 12: What are the effects of global warming?
Answer: Global warming results in the melting of polar glaciers, which leads to a rise in the sea level, causing floods in the coastal areas. Low lying coastal areas may even be permanently submerged under water.
Question 13: What is combustible substance? Give some examples.
Answer: The substance that undergoes combustion is said to be combustible substance. Some of the combustible substances are wood, coal, charcoal, paper, dry leaves, petrol etc.
Question 14: What is non-combustible substance? Give some examples.
Answer: The substance that does not burn is said to be non-combustible substance. Some of the non-combustible substances are soil, stone, glass, water etc.
Question 15: Can you burn a piece of wood by bringing a lighted matchstick near it? Explain.
Answer: The ignition temperature of a piece of wood is high which cannot be reached by the small heat produced by a burning matchstick. So, a matchstick cannot light (or burn) a piece of wood directly.
Question 16: How forest fires occur during the hottest summer days?
Or
Why do forest fires occur during hot summers?
Answer: During hot summers, sometimes the ignition temperature of dry grass in the forest is reached, which makes the dry grass catch fire. From grasses, it spreads to trees, and very soon the whole forest is on fire.
Question 17: Why does cooking oil catch fire if a frying pan is kept on the burning stove for a long time?
Answer: Cooking oil catch fire if a frying pan is kept on the burning stove for a long time because the cooking oil gets heated to its ignition temperature when kept over a burning stove for a long time.
Question 18: What chemicals can put out a fire?
Answer: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher. Another way to get CO2 is to release a lot of dry powder of chemicals like sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or potassium bicarbonate. Near the fire, these chemicals give off CO2.
Question 19: Why do you have to use paper or kerosene oil to start fire in wood or coal?
Answer: Wood or coal has a high ignition temperature, so a wood or coal fire cannot be started by using a lighted matchstick directly. Thus, we use paper or kerosene oil to start fire in wood or coal.
Question 20: Explain why we are advised not to sleep in a closed room with a coal fire burning.
Or
Why is it not advisable to sleep in a closed room with burning coal in the fireplace during winters?
Answer: Incomplete combustion of fuels gives carbon monoxide gas. It is a very poisonous gas. It is dangerous to burn coal in a closed room. The carbon monoxide gas produced can kill persons sleeping in that room.
Question 21: Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not. Give reason.
Answer: The heat supplied to the paper is transferred to aluminium pipe by conduction. So, in the presence of aluminium pipe, the ignition temperature of paper is not reached. Hence, it does not burn.
Question 22: How is fire caused by electricity extinguished?
Answer: For fires involving electrical equipment, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher. CO2, being heavier than oxygen, covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled.
Question 23: What are inflammable substances? Give examples.
Answer: The substances which have very low ignition temperature and can easily catch fire with a flame are called inflammable substances. Examples of inflammable substances are petrol, alcohol, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), etc.
Question 24: Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer: Goldsmith use the outermost zone of the flame for melting gold and silver because in the outermost zone (or non-luminous zone) of a flame, complete combustion of the fuel takes place and is the hottest part of the flame.
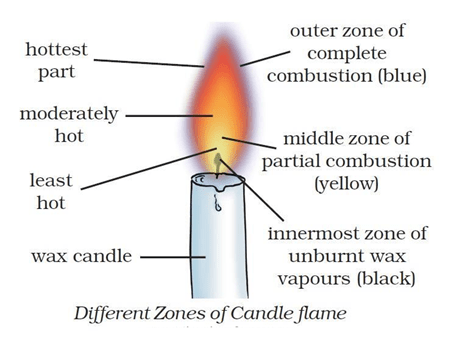
Question 25: What is the colour of the different zones of a flame?
Answer: A flame consists of three zones:
- The innermost zone of a flame is dark (or black)
- The middle zone of a flame is yellow.
- The outer zone of a flame is blue.
Question 26: It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer: It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves because it contains a lot of moisture and hence its ignition temperature is high. But dry leaves catch fire easily because it contains no moisture and hence its ignition temperature is low.
Question 27: What is spontaneous combustion? Give one example.
Answer: The type of combustion in which a material suddenly bursts into flames, without the application of any apparent cause is called spontaneous combustion. Example: Burning of white phosphorous on its own at room temperature.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: How does pouring water extinguish a fire?
Answer: Water cools the combustible material so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature. This prevents the fire from spreading. Water vapours also surround the combustible material, helping in cutting off the supply of air. So, the fire is extinguished.
Question 2: What is explosion? Explain with the help of example.
Answer: When a cracker is ignited, a sudden reaction takes place with the evolution of heat, light and sound. A large amount of gas formed in the reaction is liberated. Such a reaction is called explosion. Explosion can also take place if pressure is applied on the cracker.
Question 3: Why some substances burn with a flame while as some burn without a flame?
Answer: The substances which vapourise during burning, give flames. For example, kerosene oil and molten wax rise through the wick and are vapourised during burning and form flames. Charcoal, on the other hand, does not vapourise and so does not produce a flame.
Question 4: In an experiment 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer: The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value.
Heat produced from 4.5 kg of a fuel = 180,000 kJ
Heat produced from 1 kg of a fuel = 180,000 kJ ÷ 4.5 kg
= 40000 kJ/kg
Question 5: List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Or
What are the conditions necessary for combustion to take place?
Answer: There are three conditions which are necessary for combustion to take place. These are:
- Presence of a combustible substance (fuel)
- Presence of air or oxygen
- Heating the combustible substance to its ignition temperature
Question 6: When the clothes of a person catch fire the person is covered with a blanket to extinguish fire. Can you guess why?
Or
Why is a person whose clothes have caught fire wrapped in a thick blanket?
Or
Why do we cover a burning person in the blanket as a first aid?
Or
What should be done if the clothes of a person catch fire accidentally? Why?
Answer: When the clothes of a person catch fire the person is covered with a blanket to extinguish fire because when the burning clothes of a person are covered with a blanket, the supply of air to the burning clothes is cut off and hence the burning stops.
Question 7: What does a fire brigade do when it arrives at a place where a building is on fire?
Or
When a fire brigade arrives at a place where a building is on fire, what does it do?
Answer: It pours water on the fire. Water cools the combustible material so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature. This prevents the fire from spreading. Water vapours also surround the combustible material, helping in cutting off the supply of air. So, the fire is extinguished.
Question 8: Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer: The water in the Ramesh’s beaker will heat up in shorter time. This is because outermost part of the flame is the hottest part of the flame whereas the yellow zone of the flame (the middle zone of a flame or luminous zone) in which Abida kept the beaker produces moderate temperature.
Question 9: Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer: A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat is called combustion. The rust is formed when iron slowly combines with the oxygen present in air (in the presence of moisture) to form iron oxide. The process of rusting of iron is a slow combustion and liberates very little heat but no light.
Question 10: State any three characteristics of an ideal fuel.
Or
What are the characteristics of an ideal fuel?
Or
What is an ideal fuel?
Answer: Characteristics of an ideal fuel
- An ideal fuel is cheap, readily available, readily combustible and easy to transport.
- It has a high calorific value.
- It does not produce gases or residues that pollute the environment.
Question 11: What is acid rain? How is acid rain harmful?
Or
What are the causes and effects of acid rain?
Answer: Burning of coal and diesel release sulphur dioxide gas. It is an extremely suffocating and corrosive gas. Moreover, petrol engines give off gaseous oxides of nitrogen. Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen dissolve in rain water and form acids. Such rain is called acid rain. It is very harmful for crops, buildings and soil.
Question 12: If a can full of kerosene catches fire, what is the simplest way to put off this fire?
Answer: A small fire can be extinguished by throwing sand or soil over it. When sand is thrown over burning kerosene oil, the sand covers it like a blanket. The sand cuts off the air supply to the burning kerosene oil due to which the fire gets extinguished. For heavy fires involving inflammable materials carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher.
Question 13: What is explosive combustion? Give one example.
Answer: A very fast combustion reaction in which a large amount of heat, light and sound are produced is called explosive combustion. A large amount of gases is released quickly. It is the rapid expansion of these gases which causes a loud sound. Example: fireworks on festival days. When a cracker is ignited, a sudden reaction takes place with the evolution of heat, light and sound.
Question 14: Place a piece of burning wood or charcoal on an iron plate or Tawa. Cover it with a glass jar or a tumbler, or a transparent plastic jar. Observe what happens. Does charcoal stop burning after sometime? Can you think of the reason why it stops burning?
Answer: When a burning wood or charcoal is covered with a glass jar or a tumbler, it stops burning after sometime, that is, the charcoal fire gets extinguished after some time. This is so, because when we cover the burning wood or charcoal, the supply of supporter of combustion (i.e. air) to the burning wood or charcoal is cut off and hence the charcoal fire stops.
Question 15: Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer: Burning of fuel like petroleum releases unburnt carbon particles and gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the air. These pollutants can cause many respiratory diseases and environmental hazards. CNG produces the harmful products in very small amounts. CNG is a cleaner fuel. Thus, the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Question 16: Arrange the following fuels in the increasing order of their calorific value.
cow dung cake, petrol, wood, LPG, hydrogen
Answer:
| Fuel Calorific Value | (kJ/kg) |
| Cow dung cake | 6000-8000 |
| Wood | 17000-22000 |
| Petrol | 45000 |
| LPG | 55000 |
| Hydrogen | 150000 |
Question 17: Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer. Different Zones of candle flame is shown below
Question 18: What is matchstick made of?
Or
How do matchsticks work?
Or
Does a matchstick burn by itself? How does it burn?
Answer: These days the head of the safety match contains only antimony trisulphide and potassium chlorate. The rubbing surface has powdered glass and a little red phosphorus (which is much less dangerous). When the match is struck against the rubbing surface, some red phosphorus gets converted into white phosphorus. This immediately reacts with potassium chlorate in the matchstick head to produce enough heat to ignite antimony trisulphide and start the combustion.
Question 19: Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Or
Why is LPG a better domestic fuel than wood?
Answer: LPG and wood as fuels
- For centuries, wood was used as domestic and industrial fuel. But now it has been replaced by coal and other fuels like LPG.
- LPG has much higher calorific value than wood, so it produces much more heat on burning than an equal mass of wood.
- LPG burns without producing any smoke but burning of wood produces a lot of smoke which is very harmful for human beings.
- LPG burns completely without leaving behind any solid residue but wood leaves behind a lot of ash on burning. Thus, LPG is a cleaner fuel compared to wood.
- LPG does not causes environmental problem but cutting of trees for wood leads to deforestation which is quite harmful to the environment.
Question 19: What are the harmful effects of burning fuels?
Answer: The increasing fuel consumption has harmful effects on the environment.
- Carbon fuels like wood, coal, petroleum release unburnt carbon particles. These fine particles are dangerous pollutants causing respiratory diseases, such as asthma.
- Incomplete combustion of these fuels gives carbon monoxide gas. It is a very poisonous gas.
- Combustion of most fuels releases carbon dioxide in the environment. Increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is believed to cause global warming.
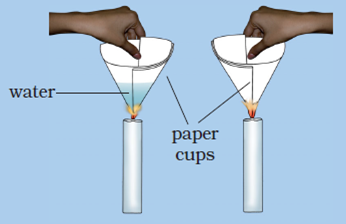
Question 20: Make two paper cups by folding a sheet of paper. Pour about 50 mL of water in one of the cups. Heat both the cups separately with a candle. What do you observe?
a. What happens to the empty paper cup and why?
b. What happens to the paper cup with water and why?
c. Does water in this cup become hot?
Answer: (a) The empty paper cup catches fire easily and starts burning because the ignition temperature of paper reaches quickly.
(b) When we heat the paper cup containing water, then the heat supplied to the paper cup is transferred to water inside it by conduction. So, in the presence of water, the ignition temperature of paper cup is not reached, and hence the paper cup does not catch fire.
(c) Yes, the water in this paper cup becomes hot gradually.
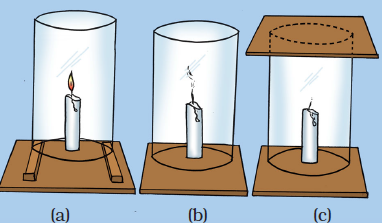
Question 21: How will you show that air is necessary for combustion?
Or
Write an activity to show that oxygen is necessary for combustion.
Or
How would you show that air is needed for combustion?
Or
How will you show that air is essential for burning fuels?
Or
What will happen if a burning candle is covered with a glass jar?
Or
Write an experiment to show that air is essential for burning.
Answer: Fix a lighted candle on a table. Put a glass chimney over the candle and rest it on a few wooden blocks in such a way that air can enter the chimney. We will see that candle burns freely in case (a) when air can enter the chimney from below. Now remove the blocks and let the chimney rest on the table.
Now, we will observe that in case (b), when air does not enter the chimney from below, the flame flickers and produces smoke. Finally, put a glass plate over the chimney. Here, in case (c), the flame finally goes off because the air is not available.
This observation shows that air is necessary for combustion (or burning) to take place.
Question 22: Explain the structure of candle flame with diagram.
Answer: A flame consists of three zones.
- The innermost zone of a flame is dark (or black) – It consists of hot, unburnt vapours of the combustible materials. It is the least hot part of the flame.
- The middle zone of a flame is yellow – It is bright and luminous. The fuel vapours burn partially in the middle zone because there is not enough air for burning in this zone. This zone produces a moderate temperature. This zone is the major part of a candle flame.
- The outer zone of a flame is blue – It is a non-luminous zone. In this zone, complete combustion of the fuel takes place because there is plenty of air around it. This zone has the highest temperature in the flame.

At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.