NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management are given below. Here we have provided the best and error-free answers to all the exercise questions that will strengthen your foundation in science. Solving NCERT questions will assist you in grasping the content in the Crop Production and Management chapter in a better way.
In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 8 science textbook. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free or can read them online.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions
Exercise Questions
Question 1: Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Answer: (a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called the crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is the preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
Question 2: Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
| (i) Kharif crops. | (e) Paddy and maize. |
| (ii) Rabi crops. | (d) Wheat, gram, pea. |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers. | (b) Urea and superphosphate. |
| (iv) Organic manure. | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes. |
Question 3: Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer:
(a) Kharif crop: Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc.
(b) Rabi crop: Wheat, gram, pea, mustard, etc.
Question 4: Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Preparation of soil: The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes which are friends of the farmer and add humus to it. Also, turning and loosening of soil brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
(b) Sowing: Sowing is an important process in crop production. First, healthy seeds are selected before sowing. After selecting healthy seeds sowing is done by either traditional methods or by using equipment’s seed drill.
(c) Weeding: Weeds are unwanted plants that grown along with crops and removal of weeds is known as weeding. Weeds can be removed either manually by using tools like khurpi or by using weedicides like 2, 4 – D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
(d) Threshing: The process of separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing. This is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher.
Question 5: Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer:
| Fertilizers | Manure |
| Fertilizer is an inorganic substance. | Manure is an organic substance. |
| Fertilizers are prepared artificially. | Manure is obtained by decomposition of animal, plant and human waste. |
| A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. | Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
| Long term usage has adverse effects on soil. | Long term usage improves soil fertility. |
| Its excessive use causes water pollution. It cannot replenish organic matter of soil. | It protects the environment and helps in recycling farm waste. |
Question 6: What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer: The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation. The two methods of irrigation which conserve water are as follows:
Sprinkler System: This system is more useful on uneven land, having fewer water supplies. In this method, water is supplied using pipes to one or more central locations within the field. When water is allowed to flow under high pressure with the help of a pump, it gets sprinkled on the crops.
Drip system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with very small holes in them to water plants drop by drop just at the base of the root. It is very efficient as water is not wasted at all.
Question 7: If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer: Wheat crops may get destroyed if sown in Kharif season because of unfavourable temperature, pests and adaptable conditions for the plants to grow. Kharif come during the rainy season, hence it is not a wise idea to grow wheat in Kharif season.
Question 8: Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer: Continuous plantation of crops in a field makes the soil poor in certain nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc. Plants require nutrients for their proper growth and functioning. When a farmer continues to grow crops one after the other, then all nutrients available in the soil reduce and the crop yield decreases automatically.
Question 9: What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer: The undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. There are many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. Weeds can be removed by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi.
Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2, 4–D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
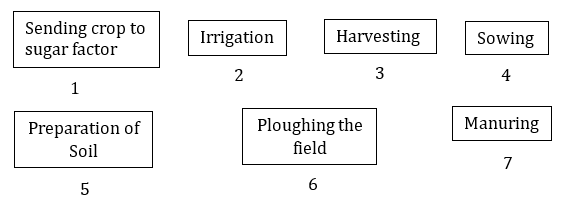
Question 10: Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
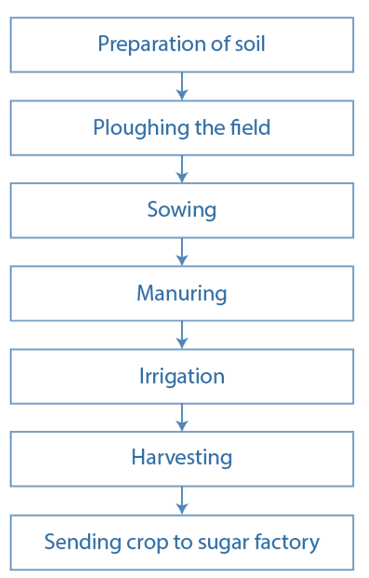
Answer:
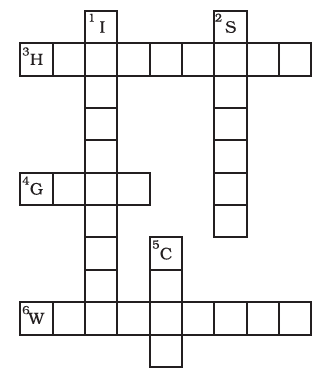
Question 11: Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
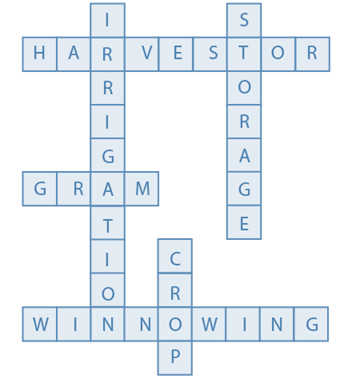
Answer:
Down
1. Irrigation
2. Stoarage
5. Crop
Across
3. Harvester
4. Gram
6. Winnowing
CBSE Class 8 NCERT solutions Science Chapter 1 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 1.1 | Agricultural Practices |
| 1.2 | Basic Practices of Crop Production |
| 1.3 | Preparation of Soil |
| 1.4 | Sowing |
| 1.5 | Adding Manure and Fertilisers |
| 1.6 | Irrigation |
| 1.7 | Protection from Weeds |
| 1.8 | Harvesting |
| 1.9 | Storage |
| 1.10 | Food from Animals |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – A Brief Discussion
CBSE Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.