NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-metals
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-metals are given below. Here we have provided the best and error-free answers to all the exercise questions that will strengthen your foundation in science. Solving NCERT questions will assist you in grasping the content in the Crop Production and Management chapter in a better way.
In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 8 science textbook. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-metals provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free or can read them online.
Materials: Metals and Non-metals Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions
Exercise Questions
Question 1: Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
(a) Zinc
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Sulphur
(d) Oxygen
Answer: (a) Zinc
Explanation: Here, Zinc is a metal with malleability and ductility whereas Phosphorus, Sulphur and Oxygen are nonmetals which lack malleability and ductility.
Question 2: Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) All metals are ductile.
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer: (c) Generally, metals are ductile.
Explanation: Ductility is a property where a substance can be drawn into thin wires, Generally, metals are ductile with mercury as the exception.
Question 3: Fill in the blanks.
(a) Phosphorus is a very _________non-metal.
(b) Metals are conductors of heat and ____________ .
(c) Iron is ____________reactive than copper.
(d) Metals react with acids to produce ____________ gas.
Answer: (a) Phosphorus is a very reactive non-metal.
(b) Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(c) Iron is more reactive than copper.
(d) Metals react with acids to produce hydrogen gas.
Question 4: Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(a) Generally, non-metals react with acids. ( )
(b) Sodium is a very reactive metal. ( )
(c) Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution. ( )
(d) Coal can be drawn into wires. ( )
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) False
(d) False
Question 5: Some properties are listed in the following table. Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of these properties.
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | ||
| 2. Hardness | ||
| 3. Malleability | ||
| 4. Ductility | ||
| 5. Heat Conduction | ||
| 6. Conduction of Electricity |
Answer:
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | Lustrous | Dull |
| 2. Hardness | Hard | Soft |
| 3. Malleability | Have property of Malleability | Do not have a property of Malleability |
| 4. Ductility | Have property of Ductility | Do not have the property of Ductility |
| 5. Heat Conduction | Good conductor of Heat | Bad Conductor of Heat |
| 6. Conduction of Electricity | Good conductor of Electricity | The bad conductor of Electricity |
Question 6: Give reasons for the following.
(a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
(b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
(c) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene
Answer: (a) Aluminium is malleable and can be drawn into thin sheets hence Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items
(b) Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Therefore, immersion rods for heating liquids are made of metallic substances.
(c) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution because Zinc is more reactive than copper.
(d) Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals. They can catch fire even when they come in contact with air. So, they have to be kept in kerosene.
Question 7: Can you store the lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer: Lemon pickle cannot be stored in aluminium utensils because lemon pickle contains acids, which can react with aluminium (metal) liberating hydrogen gas. This can lead to the spoiling of the pickle.
Question 8: Match the substances given in Column A with their uses given in Column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Gold | (a) Thermometers |
| (ii) Iron | (b) Electric wire |
| (iii) Aluminium | (c) Wrapping food |
| (iv) Carbon | (d) Jewellery |
| (v) Copper | (e) Machinery |
| (vi) Mercury | (f) Fuel |
Answer:
| A | B |
| (i) Gold | (d) Jewellery |
| (ii) Iron | (e) Machinery |
| (iii) Aluminium | (c) Wrapping food |
| (iv) Carbon | (f) Fuel |
| (v) Copper | (b) Electric wire |
| (vi) Mercury | (a) Thermometers |
Question 9: What happens when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate?
(b) Iron nails are placed in a copper sulphate solution?
Write word equations of the reactions involved.
Answer: (a) Copper does not react with dilute sulphuric acid. When concentrated sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate, copper reacts with sulphuric acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
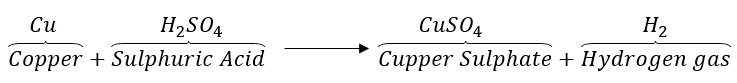
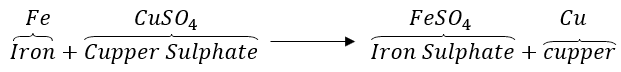
(b) The reactivity of iron is more than copper. So, iron will displace copper from copper sulphate solution. In this reaction, the blue colour of copper sulphate fades.
Question 10: Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
(a) How will she find the nature of the gas?
(b) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answer: (a) In a test tube containing gas, add a few drops of water. Now cover the test tube and shake well. After shaking, test the solution with blue litmus. It will change from blue to red. Thus, gas is acidic in nature.
(b) Charcoal reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide gas.
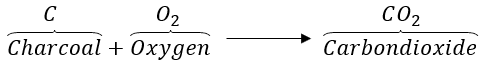
Question 11: One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight?
Answer: To polish a gold ornament, it is dipped in an acid (called Aqua Regia). The outer layer of gold dissolves in the acid and the inner shiny layer is visible. Because of loss of upper layer of jewellery, its weight is reduced.
CBSE Class 8 NCERT solutions Science Chapter 4 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 4.1 | Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals |
| 4.2 | Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals |
| 4.3 | Uses of Metals and Non-metals |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – A Brief Discussion
CBSE Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 4 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.