NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (biology) Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 5 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Textbook Questions and Answers
INTEXT QUESTIONS
PAGE NO 59
Question 1: Who discovered cells and how?
Answer: Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice.
Question 2: Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: A cell is capable of carrying out all the life functions; such as nutrition, excretion, respiration, etc. Hence a cell is called the functional unit of life. Additionally, the cell is the smallest unit of life and all the living beings are made up of cells. Hence a cell is called the structural unit of life.
PAGE NO. 61
Question 1: How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer: Substances move in and out of the cell because of diffusion. Diffusion is the random movement of particles in order to attain concentration equilibrium. The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane is called osmosis. It is important to note that plasma membrane is a semi-permeable membrane. Water always moves from high water concentration to low water concentration.
or
CO2 moves by diffusion – These cellular waste accumulates in high concentrations in the cell, whereas the concentration of CO2 in the external surroundings is comparatively lower. This difference in the concentration level inside and out of the cell causes the CO2 to diffuse from a region of higher(within the cell) to a lower concentration.
H2O diffuses by osmosis through the cell membrane. It moves from a region of higher concentration to a lower concentrated region through a selectively permeable membrane until equilibrium is reached.
Question 2: Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer: Plasma membrane allows passage to some selected substances. Hence it is called a selectively permeable or semi-permeable membrane.
or
The cell membrane or the plasma membrane is known as a selectively permeable membrane because it regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This means that the plasma membrane allows the entry of only some substances and prevents the movement of some other materials.
PAGE NO 63
Question 1: Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1. Size: generally small (1-10μm) | 1. Size: generally large (5-100μm) |
| 2. Nuclear region:________________ and known as _________________ | 2. Nuclear region: well defined and surround by a nuclear membrane. |
| 3. Chromosome: Single | 3. More than one chromosome |
| 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles absent | 4. _________________ |
Answer:
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1. Size: generally small (1-10μm) | 1. Size: generally large (5-100μm) |
| 2. Nuclear region: poorly defined because of absence of nuclear membrane and known as nucleoid | 2. Nuclear region: well defined and surround by a nuclear membrane and known as nucleoid. |
| 3. Chromosome: Single | 3. More than one chromosome |
| 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles absent | 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles such as Mitochondria, plastids, etc., are present. |
PAGE NO 65
Question 1: Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer: Mitochondria and plastids are the two organelles that contain their own genetic material. Both these organelles have their own DNA and ribosomes.
Question 2: If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer: Cell is the smallest unit of life, which is capable of all living functions. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, then the ability of the cell to perform all living functions such as respiration, nutrition, excretion, etc. would be affected.
Question 3: Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer: The lysosomes contain very powerful hydrolytic enzymes which are capable of breaking down organic matter. For example, when a cell gets damaged, then lysosomes burst and enzymes digest their own cell. Hence, the lysosomes are known as ‘suicide bags’ of cells
Question 4: Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Answer: Ribosomes are the site for protein synthesis. Ribosomes are very small structures found either in a free state, suspended in the cytoplasm, or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. They are composed of ribonucleic acids and proteins.
EXERCISES
Question 1: Make a comparison to write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer: The cells of animals and plants have the following differences:
| Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
| 1. Animal cells are generally small in size. | 1. Plant cells are larger than animal cells. |
| 2. Cell wall is absent. | 2. The plasma membrane of plant cells is surrounded by a rigid cell wall of cellulose. |
| 3. Except the protozoan Euglena, no animal cell possesses plastids. | 3. Plastids are present. |
| 4. Vacuoles in animal cells are many, small and temporary. | 4. Most mature plant cells have a permanent and large central sap vacuole. |
| 5. Animal cells have a single highly complex and prominent Golgi apparatus. | 5. Plant cells have many simpler units of Golgi apparatus, called dictyosomes. |
| 6. Animal cells have centrosome and centrioles. | 6. Plant cells lack centrosome and centrioles. |
Question 2: How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer: Difference between prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell:
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1. Cell size is generally small (1 – 10 µm). | 1. Cell is generally large (5 – 100 µm). |
| 2. Nuclear region is called nucleoid and is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. | 2. Nuclear material is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. . |
| 3. Only a single chromosome is present. | 3. More than one chromosome is present. |
| 4. Nucleolus is absent. | 4. Nucleolus is present. |
| 5. Membrane bound cell organelles are absent. | 5.Membrane bound cell organelles. |
| 6. Cell division by fission or budding (no mitosis). | 6. Cell division mitotic or meiotic. |
Question 3: What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer: Plasma membrane provides a container for the cell organelles and cytoplasm. Moreover, plasma membrane also protects the contents of a cell from external environment. In case the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down, the cell contents would be exposed to the external environment. This would prove lethal for the cell and the cell would cease to exist.
Question 4: What would happen to the life of a cell if there is no Golgi apparatus?
Answer: Golgi apparatus plays the important role of packaging various substances for further use or for storage. If there was no Golgi apparatus, various substances would not be in a position to be transformed in proper forms for further use. Certain substances; like protein and lipid are important for the formation of plasma membrane and hence absence of Golgi apparatus will hamper the formation of new cells during cell division.
Question 5: Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of cells. Mitochondria create energy for the cell, and this process of creating energy for the cell is known as cellular respiration. Most chemical reactions involved in cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria. The energy required for various chemical activities needed for life is released by the mitochondria in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules. For this reason, mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of cells
Question 6: Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer: Lipids are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. Protein is synthesized in ribosomes which are usually present on the rough ER.
Question 7: How does Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer: Amoeba obtains its food through a process called phagocytosis. The cell membrane of amoeba is projected into numerous finger-like outgrowths; called pseudopodia. Amoeba surrounds a food particle by pseudopodia and makes a food vacuole; after engulfing the food.
Question 8: What is osmosis?
Answer: The process of movement of a water molecule from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane is known as osmosis.
Question 9: Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
Answer:
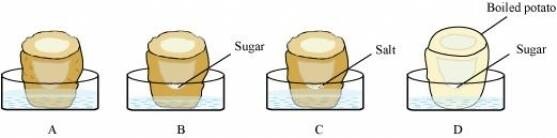
Experimental set up
(i) Water gathers in the hollowed portions of set-up B and C because water enters the potato as a result of osmosis. Since the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell, the water moves inside by osmosis. Hence, water gathers in the hollowed portions of the potato cup.
(ii) Potato A in the experiment acts as a control set-up. No water gathers in the hollowed portions of potato A.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed portions of potato A because potato cup A is empty. It is a control set-up in the experiment.
Water is not able to enter potato D because the potato used here is boiled. Boiling denatures the proteins present in the cell membrane and thus, disrupts the cell membrane. For osmosis, a semi-permeable membrane is required, which is disrupted in this case. Therefore, osmosis will not occur. Hence, water does not enter the boiled potato cup.
Question 10: Which type of cell division is required for growth and repair of body and which type is involved in formation of gametes?
Answer: There are two ways in which a cell divides:
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
Mitosis is the type of cell division that is involved in the growth and repair of body whereas meiosis is a type of cell division which results in the formation of gametes.
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 5.1 | What are Living Organisms Made Up of? |
| 5.2.2 | Cell Wall |
| 5.2.3 | Nucleus |
| 5.2.4 | Cytoplasm |
| 5.2.5 | Cell Organelles |